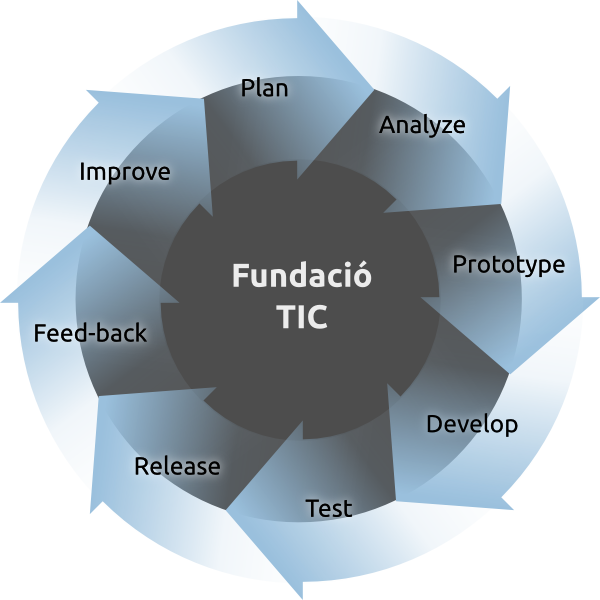
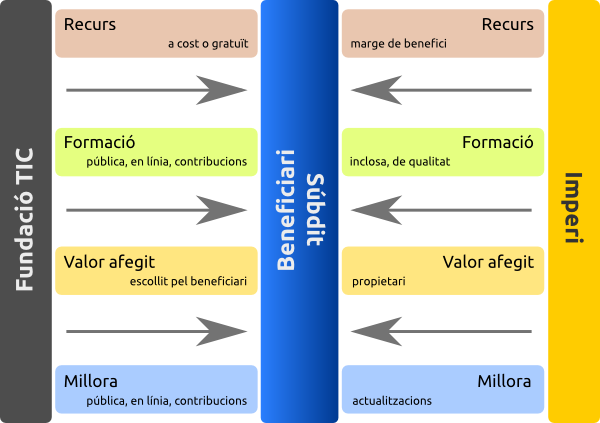
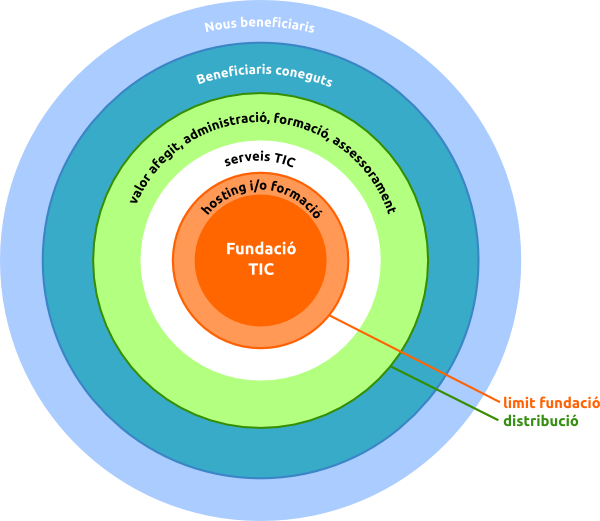
:8ball:
:art:
:badminton:
:banjo:
:baseball:
:basketball:
:bow_and_arrow:
:bowling:
:boxing_glove:
:chess_pawn:
:circus_tent:
:clapper:
:cricket_game:
:curling_stone:
:dart:
:drum:
:field_hockey:
:first_place:
:fishing_pole_and_fish:
:flying_disc:
:football:
:game_die:
:goal:
:golf:
:guitar:
:headphones:
:hockey:
:horse_racing:
:horse_racing_tone1:
:horse_racing_tone2:
:horse_racing_tone3:
:horse_racing_tone4:
:horse_racing_tone5:
:ice_skate:
:jigsaw:
:kite:
:lacrosse:
:man_biking:
:man_biking_tone1:
:man_biking_tone2:
:man_biking_tone3:
:man_biking_tone4:
:man_biking_tone5:
:man_bouncing_ball:
:man_bouncing_ball_tone1:
:man_bouncing_ball_tone2:
:man_bouncing_ball_tone3:
:man_bouncing_ball_tone4:
:man_bouncing_ball_tone5:
:man_cartwheeling:
:man_cartwheeling_tone1:
:man_cartwheeling_tone2:
:man_cartwheeling_tone3:
:man_cartwheeling_tone4:
:man_cartwheeling_tone5:
:man_climbing:
:man_climbing_tone1:
:man_climbing_tone2:
:man_climbing_tone3:
:man_climbing_tone4:
:man_climbing_tone5:
:man_golfing:
:man_golfing_tone1:
:man_golfing_tone2:
:man_golfing_tone3:
:man_golfing_tone4:
:man_golfing_tone5:
:man_in_lotus_position:
:man_in_lotus_position_tone1:
:man_in_lotus_position_tone2:
:man_in_lotus_position_tone3:
:man_in_lotus_position_tone4:
:man_in_lotus_position_tone5:
:man_juggling:
:man_juggling_tone1:
:man_juggling_tone2:
:man_juggling_tone3:
:man_juggling_tone4:
:man_juggling_tone5:
:man_lifting_weights:
:man_lifting_weights_tone1:
:man_lifting_weights_tone2:
:man_lifting_weights_tone3:
:man_lifting_weights_tone4:
:man_lifting_weights_tone5:
:man_mountain_biking:
:man_mountain_biking_tone1:
:man_mountain_biking_tone2:
:man_mountain_biking_tone3:
:man_mountain_biking_tone4:
:man_mountain_biking_tone5:
:man_playing_handball:
:man_playing_handball_tone1:
:man_playing_handball_tone2:
:man_playing_handball_tone3:
:man_playing_handball_tone4:
:man_playing_handball_tone5:
:man_playing_water_polo:
:man_playing_water_polo_tone1:
:man_playing_water_polo_tone2:
:man_playing_water_polo_tone3:
:man_playing_water_polo_tone4:
:man_playing_water_polo_tone5:
:man_rowing_boat:
:man_rowing_boat_tone1:
:man_rowing_boat_tone2:
:man_rowing_boat_tone3:
:man_rowing_boat_tone4:
:man_rowing_boat_tone5:
:man_surfing:
:man_surfing_tone1:
:man_surfing_tone2:
:man_surfing_tone3:
:man_surfing_tone4:
:man_surfing_tone5:
:man_swimming:
:man_swimming_tone1:
:man_swimming_tone2:
:man_swimming_tone3:
:man_swimming_tone4:
:man_swimming_tone5:
:martial_arts_uniform:
:medal:
:men_wrestling:
:microphone:
:military_medal:
:musical_keyboard:
:musical_score:
:parachute:
:people_wrestling:
:performing_arts:
:person_biking:
:person_biking_tone1:
:person_biking_tone2:
:person_biking_tone3:
:person_biking_tone4:
:person_biking_tone5:
:person_bouncing_ball:
:person_bouncing_ball_tone1:
:person_bouncing_ball_tone2:
:person_bouncing_ball_tone3:
:person_bouncing_ball_tone4:
:person_bouncing_ball_tone5:
:person_climbing:
:person_climbing_tone1:
:person_climbing_tone2:
:person_climbing_tone3:
:person_climbing_tone4:
:person_climbing_tone5:
:person_doing_cartwheel:
:person_doing_cartwheel_tone1:
:person_doing_cartwheel_tone2:
:person_doing_cartwheel_tone3:
:person_doing_cartwheel_tone4:
:person_doing_cartwheel_tone5:
:person_fencing:
:person_golfing:
:person_golfing_tone1:
:person_golfing_tone2:
:person_golfing_tone3:
:person_golfing_tone4:
:person_golfing_tone5:
:person_in_lotus_position:
:person_in_lotus_position_tone1:
:person_in_lotus_position_tone2:
:person_in_lotus_position_tone3:
:person_in_lotus_position_tone4:
:person_in_lotus_position_tone5:
:person_juggling:
:person_juggling_tone1:
:person_juggling_tone2:
:person_juggling_tone3:
:person_juggling_tone4:
:person_juggling_tone5:
:person_lifting_weights:
:person_lifting_weights_tone1:
:person_lifting_weights_tone2:
:person_lifting_weights_tone3:
:person_lifting_weights_tone4:
:person_lifting_weights_tone5:
:person_mountain_biking:
:person_mountain_biking_tone1:
:person_mountain_biking_tone2:
:person_mountain_biking_tone3:
:person_mountain_biking_tone4:
:person_mountain_biking_tone5:
:person_playing_handball:
:person_playing_handball_tone1:
:person_playing_handball_tone2:
:person_playing_handball_tone3:
:person_playing_handball_tone4:
:person_playing_handball_tone5:
:person_playing_water_polo:
:person_playing_water_polo_tone1:
:person_playing_water_polo_tone2:
:person_playing_water_polo_tone3:
:person_playing_water_polo_tone4:
:person_playing_water_polo_tone5:
:person_rowing_boat:
:person_rowing_boat_tone1:
:person_rowing_boat_tone2:
:person_rowing_boat_tone3:
:person_rowing_boat_tone4:
:person_rowing_boat_tone5:
:person_surfing:
:person_surfing_tone1:
:person_surfing_tone2:
:person_surfing_tone3:
:person_surfing_tone4:
:person_surfing_tone5:
:person_swimming:
:person_swimming_tone1:
:person_swimming_tone2:
:person_swimming_tone3:
:person_swimming_tone4:
:person_swimming_tone5:
:ping_pong:
:reminder_ribbon:
:rosette:
:rugby_football:
:running_shirt_with_sash:
:saxophone:
:second_place:
:skateboard:
:ski:
:skier:
:sled:
:slot_machine:
:snowboarder:
:snowboarder_tone1:
:snowboarder_tone2:
:snowboarder_tone3:
:snowboarder_tone4:
:snowboarder_tone5:
:soccer:
:softball:
:tennis:
:third_place:
:ticket:
:tickets:
:trophy:
:trumpet:
:video_game:
:violin:
:volleyball:
:woman_biking:
:woman_biking_tone1:
:woman_biking_tone2:
:woman_biking_tone3:
:woman_biking_tone4:
:woman_biking_tone5:
:woman_bouncing_ball:
:woman_bouncing_ball_tone1:
:woman_bouncing_ball_tone2:
:woman_bouncing_ball_tone3:
:woman_bouncing_ball_tone4:
:woman_bouncing_ball_tone5:
:woman_cartwheeling:
:woman_cartwheeling_tone1:
:woman_cartwheeling_tone2:
:woman_cartwheeling_tone3:
:woman_cartwheeling_tone4:
:woman_cartwheeling_tone5:
:woman_climbing:
:woman_climbing_tone1:
:woman_climbing_tone2:
:woman_climbing_tone3:
:woman_climbing_tone4:
:woman_climbing_tone5:
:woman_golfing:
:woman_golfing_tone1:
:woman_golfing_tone2:
:woman_golfing_tone3:
:woman_golfing_tone4:
:woman_golfing_tone5:
:woman_in_lotus_position:
:woman_in_lotus_position_tone1:
:woman_in_lotus_position_tone2:
:woman_in_lotus_position_tone3:
:woman_in_lotus_position_tone4:
:woman_in_lotus_position_tone5:
:woman_juggling:
:woman_juggling_tone1:
:woman_juggling_tone2:
:woman_juggling_tone3:
:woman_juggling_tone4:
:woman_juggling_tone5:
:woman_lifting_weights:
:woman_lifting_weights_tone1:
:woman_lifting_weights_tone2:
:woman_lifting_weights_tone3:
:woman_lifting_weights_tone4:
:woman_lifting_weights_tone5:
:woman_mountain_biking:
:woman_mountain_biking_tone1:
:woman_mountain_biking_tone2:
:woman_mountain_biking_tone3:
:woman_mountain_biking_tone4:
:woman_mountain_biking_tone5:
:woman_playing_handball:
:woman_playing_handball_tone1:
:woman_playing_handball_tone2:
:woman_playing_handball_tone3:
:woman_playing_handball_tone4:
:woman_playing_handball_tone5:
:woman_playing_water_polo:
:woman_playing_water_polo_tone1:
:woman_playing_water_polo_tone2:
:woman_playing_water_polo_tone3:
:woman_playing_water_polo_tone4:
:woman_playing_water_polo_tone5:
:woman_rowing_boat:
:woman_rowing_boat_tone1:
:woman_rowing_boat_tone2:
:woman_rowing_boat_tone3:
:woman_rowing_boat_tone4:
:woman_rowing_boat_tone5:
:woman_surfing:
:woman_surfing_tone1:
:woman_surfing_tone2:
:woman_surfing_tone3:
:woman_surfing_tone4:
:woman_surfing_tone5:
:woman_swimming:
:woman_swimming_tone1:
:woman_swimming_tone2:
:woman_swimming_tone3:
:woman_swimming_tone4:
:woman_swimming_tone5:
:women_wrestling:
:yo_yo:
:checkered_flag:
:crossed_flags:
:england:
:flag_ac:
:flag_ad:
:flag_ae:
:flag_af:
:flag_ag:
:flag_ai:
:flag_al:
:flag_am:
:flag_ao:
:flag_aq:
:flag_ar:
:flag_as:
:flag_at:
:flag_au:
:flag_aw:
:flag_ax:
:flag_az:
:flag_ba:
:flag_bb:
:flag_bd:
:flag_be:
:flag_bf:
:flag_bg:
:flag_bh:
:flag_bi:
:flag_bj:
:flag_bl:
:flag_black:
:flag_bm:
:flag_bn:
:flag_bo:
:flag_bq:
:flag_br:
:flag_bs:
:flag_bt:
:flag_bv:
:flag_bw:
:flag_by:
:flag_bz:
:flag_ca:
:flag_cc:
:flag_cd:
:flag_cf:
:flag_cg:
:flag_ch:
:flag_ci:
:flag_ck:
:flag_cl:
:flag_cm:
:flag_cn:
:flag_co:
:flag_cp:
:flag_cr:
:flag_cu:
:flag_cv:
:flag_cw:
:flag_cx:
:flag_cy:
:flag_cz:
:flag_de:
:flag_dg:
:flag_dj:
:flag_dk:
:flag_dm:
:flag_do:
:flag_dz:
:flag_ea:
:flag_ec:
:flag_ee:
:flag_eg:
:flag_eh:
:flag_er:
:flag_es:
:flag_et:
:flag_eu:
:flag_fi:
:flag_fj:
:flag_fk:
:flag_fm:
:flag_fo:
:flag_fr:
:flag_ga:
:flag_gb:
:flag_gd:
:flag_ge:
:flag_gf:
:flag_gg:
:flag_gh:
:flag_gi:
:flag_gl:
:flag_gm:
:flag_gn:
:flag_gp:
:flag_gq:
:flag_gr:
:flag_gs:
:flag_gt:
:flag_gu:
:flag_gw:
:flag_gy:
:flag_hk:
:flag_hm:
:flag_hn:
:flag_hr:
:flag_ht:
:flag_hu:
:flag_ic:
:flag_id:
:flag_ie:
:flag_il:
:flag_im:
:flag_in:
:flag_io:
:flag_iq:
:flag_ir:
:flag_is:
:flag_it:
:flag_je:
:flag_jm:
:flag_jo:
:flag_jp:
:flag_ke:
:flag_kg:
:flag_kh:
:flag_ki:
:flag_km:
:flag_kn:
:flag_kp:
:flag_kr:
:flag_kw:
:flag_ky:
:flag_kz:
:flag_la:
:flag_lb:
:flag_lc:
:flag_li:
:flag_lk:
:flag_lr:
:flag_ls:
:flag_lt:
:flag_lu:
:flag_lv:
:flag_ly:
:flag_ma:
:flag_mc:
:flag_md:
:flag_me:
:flag_mf:
:flag_mg:
:flag_mh:
:flag_mk:
:flag_ml:
:flag_mm:
:flag_mn:
:flag_mo:
:flag_mp:
:flag_mq:
:flag_mr:
:flag_ms:
:flag_mt:
:flag_mu:
:flag_mv:
:flag_mw:
:flag_mx:
:flag_my:
:flag_mz:
:flag_na:
:flag_nc:
:flag_ne:
:flag_nf:
:flag_ng:
:flag_ni:
:flag_nl:
:flag_no:
:flag_np:
:flag_nr:
:flag_nu:
:flag_nz:
:flag_om:
:flag_pa:
:flag_pe:
:flag_pf:
:flag_pg:
:flag_ph:
:flag_pk:
:flag_pl:
:flag_pm:
:flag_pn:
:flag_pr:
:flag_ps:
:flag_pt:
:flag_pw:
:flag_py:
:flag_qa:
:flag_re:
:flag_ro:
:flag_rs:
:flag_ru:
:flag_rw:
:flag_sa:
:flag_sb:
:flag_sc:
:flag_sd:
:flag_se:
:flag_sg:
:flag_sh:
:flag_si:
:flag_sj:
:flag_sk:
:flag_sl:
:flag_sm:
:flag_sn:
:flag_so:
:flag_sr:
:flag_ss:
:flag_st:
:flag_sv:
:flag_sx:
:flag_sy:
:flag_sz:
:flag_ta:
:flag_tc:
:flag_td:
:flag_tf:
:flag_tg:
:flag_th:
:flag_tj:
:flag_tk:
:flag_tl:
:flag_tm:
:flag_tn:
:flag_to:
:flag_tr:
:flag_tt:
:flag_tv:
:flag_tw:
:flag_tz:
:flag_ua:
:flag_ug:
:flag_um:
:flag_us:
:flag_uy:
:flag_uz:
:flag_va:
:flag_vc:
:flag_ve:
:flag_vg:
:flag_vi:
:flag_vn:
:flag_vu:
:flag_wf:
:flag_white:
:flag_ws:
:flag_xk:
:flag_ye:
:flag_yt:
:flag_za:
:flag_zm:
:flag_zw:
:pirate_flag:
:rainbow_flag:
:scotland:
:triangular_flag_on_post:
:united_nations:
:wales:
:apple:
:avocado:
:baby_bottle:
:bacon:
:bagel:
:banana:
:beer:
:beers:
:bento:
:beverage_box:
:birthday:
:bowl_with_spoon:
:bread:
:broccoli:
:burrito:
:butter:
:cake:
:candy:
:canned_food:
:carrot:
:champagne:
:champagne_glass:
:cheese:
:cherries:
:chestnut:
:chocolate_bar:
:chopsticks:
:cocktail:
:coconut:
:coffee:
:cookie:
:cooking:
:corn:
:croissant:
:cucumber:
:cup_with_straw:
:cupcake:
:curry:
:custard:
:cut_of_meat:
:dango:
:doughnut:
:dumpling:
:egg:
:eggplant:
:falafel:
:fish_cake:
:fork_and_knife:
:fork_knife_plate:
:fortune_cookie:
:french_bread:
:fried_shrimp:
:fries:
:garlic:
:grapes:
:green_apple:
:hamburger:
:honey_pot:
:hot_pepper:
:hotdog:
:ice_cream:
:ice_cube:
:icecream:
:kiwi:
:leafy_green:
:lemon:
:lollipop:
:mango:
:mate:
:meat_on_bone:
:melon:
:milk:
:moon_cake:
:oden:
:onion:
:pancakes:
:peach:
:peanuts:
:pear:
:pie:
:pineapple:
:pizza:
:popcorn:
:potato:
:poultry_leg:
:pretzel:
:ramen:
:rice:
:rice_ball:
:rice_cracker:
:sake:
:salad:
:salt:
:sandwich:
:shallow_pan_of_food:
:shaved_ice:
:spaghetti:
:spoon:
:stew:
:strawberry:
:stuffed_flatbread:
:sushi:
:sweet_potato:
:taco:
:takeout_box:
:tangerine:
:tea:
:tomato:
:tropical_drink:
:tumbler_glass:
:waffle:
:watermelon:
:wine_glass:
:tone1:
:tone2:
:tone3:
:tone4:
:tone5:
:ant:
:baby_chick:
:badger:
:bamboo:
:bat:
:bear:
:bee:
:beetle:
:bird:
:blossom:
:blowfish:
:boar:
:boom:
:bouquet:
:bug:
:butterfly:
:cactus:
:camel:
:cat2:
:cat:
:cherry_blossom:
:chicken:
:chipmunk:
:christmas_tree:
:cloud:
:cloud_lightning:
:cloud_rain:
:cloud_snow:
:cloud_tornado:
:comet:
:cow2:
:cow:
:crab:
:crescent_moon:
:cricket:
:crocodile:
:dash:
:deciduous_tree:
:deer:
:dizzy:
:dog2:
:dog:
:dolphin:
:dove:
:dragon:
:dragon_face:
:dromedary_camel:
:droplet:
:duck:
:eagle:
:ear_of_rice:
:earth_africa:
:earth_americas:
:earth_asia:
:elephant:
:evergreen_tree:
:fallen_leaf:
:feet:
:fire:
:first_quarter_moon:
:first_quarter_moon_with_face:
:fish:
:flamingo:
:fog:
:four_leaf_clover:
:fox:
:frog:
:full_moon:
:full_moon_with_face:
:giraffe:
:goat:
:gorilla:
:guide_dog:
:hamster:
:hatched_chick:
:hatching_chick:
:hear_no_evil:
:hedgehog:
:herb:
:hibiscus:
:hippopotamus:
:horse:
:kangaroo:
:koala:
:last_quarter_moon:
:last_quarter_moon_with_face:
:leaves:
:leopard:
:lion_face:
:lizard:
:llama:
:lobster:
:maple_leaf:
:monkey:
:monkey_face:
:mosquito:
:mouse2:
:mouse:
:mushroom:
:new_moon:
:new_moon_with_face:
:ocean:
:octopus:
:orangutan:
:otter:
:owl:
:ox:
:oyster:
:palm_tree:
:panda_face:
:parrot:
:partly_sunny:
:peacock:
:penguin:
:pig2:
:pig:
:pig_nose:
:poodle:
:rabbit2:
:rabbit:
:raccoon:
:racehorse:
:rainbow:
:ram:
:rat:
:rhino:
:ringed_planet:
:rooster:
:rose:
:sauropod:
:scorpion:
:see_no_evil:
:seedling:
:service_dog:
:shamrock:
:shark:
:sheep:
:shell:
:shrimp:
:skunk:
:sloth:
:snail:
:snake:
:snowflake:
:snowman2:
:snowman:
:sparkles:
:speak_no_evil:
:spider:
:spider_web:
:squid:
:star2:
:star:
:sun_with_face:
:sunflower:
:sunny:
:swan:
:sweat_drops:
:t_rex:
:tanabata_tree:
:thunder_cloud_rain:
:tiger2:
:tiger:
:tropical_fish:
:tulip:
:turkey:
:turtle:
:umbrella2:
:umbrella:
:unicorn:
:waning_crescent_moon:
:waning_gibbous_moon:
:water_buffalo:
:waxing_crescent_moon:
:waxing_gibbous_moon:
:whale2:
:whale:
:white_sun_cloud:
:white_sun_rain_cloud:
:white_sun_small_cloud:
:wilted_rose:
:wind_blowing_face:
:wolf:
:zap:
:zebra:
:abacus:
:adhesive_bandage:
:alarm_clock:
:alembic:
:amphora:
:axe:
:balloon:
:ballot_box:
:bar_chart:
:barber:
:basket:
:bath:
:bath_tone1:
:bath_tone2:
:bath_tone3:
:bath_tone4:
:bath_tone5:
:bathtub:
:battery:
:bed:
:bellhop:
:black_nib:
:blue_book:
:bomb:
:book:
:bookmark:
:bookmark_tabs:
:books:
:bricks:
:broom:
:bulb:
:calendar:
:calendar_spiral:
:calling:
:camera:
:camera_with_flash:
:candle:
:card_box:
:card_index:
:cd:
:chains:
:chair:
:chart_with_downwards_trend:
:chart_with_upwards_trend:
:clipboard:
:clock:
:closed_book:
:closed_lock_with_key:
:coffin:
:compass:
:compression:
:computer:
:confetti_ball:
:control_knobs:
:couch:
:crayon:
:credit_card:
:crossed_swords:
:crystal_ball:
:dagger:
:date:
:desktop:
:dividers:
:diya_lamp:
:dna:
:dollar:
:dolls:
:door:
:drop_of_blood:
:dvd:
:e-mail:
:electric_plug:
:envelope:
:envelope_with_arrow:
:euro:
:fax:
:file_cabinet:
:file_folder:
:film_frames:
:fire_extinguisher:
:firecracker:
:flags:
:flashlight:
:floppy_disk:
:frame_photo:
:gear:
:gem:
:gift:
:green_book:
:gun:
:hammer:
:hammer_pick:
:hole:
:hourglass:
:hourglass_flowing_sand:
:inbox_tray:
:incoming_envelope:
:iphone:
:izakaya_lantern:
:joystick:
:key2:
:key:
:keyboard:
:knife:
:label:
:ledger:
:level_slider:
:link:
:lock:
:lock_with_ink_pen:
:love_letter:
:mag:
:mag_right:
:magnet:
:mailbox:
:mailbox_closed:
:mailbox_with_mail:
:mailbox_with_no_mail:
:microbe:
:microphone2:
:microscope:
:minidisc:
:money_with_wings:
:moneybag:
:mouse_three_button:
:movie_camera:
:nazar_amulet:
:newspaper2:
:newspaper:
:notebook:
:notebook_with_decorative_cover:
:notepad_spiral:
:nut_and_bolt:
:oil:
:open_file_folder:
:orange_book:
:outbox_tray:
:package:
:page_facing_up:
:page_with_curl:
:pager:
:paintbrush:
:paperclip:
:paperclips:
:pen_ballpoint:
:pen_fountain:
:pencil2:
:pencil:
:person_in_bed_tone1:
:person_in_bed_tone2:
:person_in_bed_tone3:
:person_in_bed_tone4:
:person_in_bed_tone5:
:petri_dish:
:pick:
:pill:
:postal_horn:
:postbox:
:potable_water:
:pound:
:prayer_beads:
:printer:
:probing_cane:
:projector:
:pushpin:
:radio:
:razor:
:receipt:
:red_envelope:
:ribbon:
:roll_of_paper:
:round_pushpin:
:safety_pin:
:satellite:
:scales:
:scissors:
:scroll:
:shield:
:shopping_bags:
:shopping_cart:
:shower:
:sleeping_accommodation:
:smoking:
:soap:
:sponge:
:squeeze_bottle:
:stethoscope:
:stopwatch:
:straight_ruler:
:syringe:
:tada:
:teddy_bear:
:telephone:
:telephone_receiver:
:telescope:
:test_tube:
:thermometer:
:timer:
:toilet:
:toolbox:
:tools:
:trackball:
:triangular_ruler:
:tv:
:unlock:
:urn:
:vhs:
:video_camera:
:wastebasket:
:watch:
:wind_chime:
:wrench:
:yen:
:adult:
:adult_tone1:
:adult_tone2:
:adult_tone3:
:adult_tone4:
:adult_tone5:
:alien:
:angel:
:angel_tone1:
:angel_tone2:
:angel_tone3:
:angel_tone4:
:angel_tone5:
:angry:
:anguished:
:astonished:
:athletic_shoe:
:baby:
:baby_tone1:
:baby_tone2:
:baby_tone3:
:baby_tone4:
:baby_tone5:
:bald:
:ballet_shoes:
:bearded_person:
:bearded_person_tone1:
:bearded_person_tone2:
:bearded_person_tone3:
:bearded_person_tone4:
:bearded_person_tone5:
:bikini:
:billed_cap:
:blond-haired_man:
:blond-haired_man_tone1:
:blond-haired_man_tone2:
:blond-haired_man_tone3:
:blond-haired_man_tone4:
:blond-haired_man_tone5:
:blond-haired_woman:
:blond-haired_woman_tone1:
:blond-haired_woman_tone2:
:blond-haired_woman_tone3:
:blond-haired_woman_tone4:
:blond-haired_woman_tone5:
:blond_haired_person:
:blond_haired_person_tone1:
:blond_haired_person_tone2:
:blond_haired_person_tone3:
:blond_haired_person_tone4:
:blond_haired_person_tone5:
:blush:
:bone:
:boot:
:boy:
:boy_tone1:
:boy_tone2:
:boy_tone3:
:boy_tone4:
:boy_tone5:
:brain:
:breast_feeding:
:breast_feeding_tone1:
:breast_feeding_tone2:
:breast_feeding_tone3:
:breast_feeding_tone4:
:breast_feeding_tone5:
:bride_with_veil:
:bride_with_veil_tone1:
:bride_with_veil_tone2:
:bride_with_veil_tone3:
:bride_with_veil_tone4:
:bride_with_veil_tone5:
:briefcase:
:briefs:
:bust_in_silhouette:
:busts_in_silhouette:
:call_me:
:call_me_tone1:
:call_me_tone2:
:call_me_tone3:
:call_me_tone4:
:call_me_tone5:
:child:
:child_tone1:
:child_tone2:
:child_tone3:
:child_tone4:
:child_tone5:
:clap:
:clap_tone1:
:clap_tone2:
:clap_tone3:
:clap_tone4:
:clap_tone5:
:closed_umbrella:
:clown:
:coat:
:cold_face:
:cold_sweat:
:confounded:
:confused:
:construction_worker:
:construction_worker_tone1:
:construction_worker_tone2:
:construction_worker_tone3:
:construction_worker_tone4:
:construction_worker_tone5:
:couple:
:couple_mm:
:couple_with_heart:
:couple_with_heart_woman_man:
:couple_ww:
:couplekiss:
:cowboy:
:crown:
:cry:
:crying_cat_face:
:curly_haired:
:dancer:
:dancer_tone1:
:dancer_tone2:
:dancer_tone3:
:dancer_tone4:
:dancer_tone5:
:dark_sunglasses:
:deaf_man:
:deaf_man_tone1:
:deaf_man_tone2:
:deaf_man_tone3:
:deaf_man_tone4:
:deaf_man_tone5:
:deaf_person:
:deaf_person_tone1:
:deaf_person_tone2:
:deaf_person_tone3:
:deaf_person_tone4:
:deaf_person_tone5:
:deaf_woman:
:deaf_woman_tone1:
:deaf_woman_tone2:
:deaf_woman_tone3:
:deaf_woman_tone4:
:deaf_woman_tone5:
:detective:
:detective_tone1:
:detective_tone2:
:detective_tone3:
:detective_tone4:
:detective_tone5:
:disappointed:
:disappointed_relieved:
:diving_mask:
:dizzy_face:
:dress:
:drooling_face:
:ear:
:ear_tone1:
:ear_tone2:
:ear_tone3:
:ear_tone4:
:ear_tone5:
:ear_with_hearing_aid:
:ear_with_hearing_aid_tone1:
:ear_with_hearing_aid_tone2:
:ear_with_hearing_aid_tone3:
:ear_with_hearing_aid_tone4:
:ear_with_hearing_aid_tone5:
:elf:
:elf_tone1:
:elf_tone2:
:elf_tone3:
:elf_tone4:
:elf_tone5:
:exploding_head:
:expressionless:
:eye:
:eyeglasses:
:eyes:
:face_vomiting:
:face_with_hand_over_mouth:
:face_with_monocle:
:face_with_raised_eyebrow:
:face_with_symbols_over_mouth:
:fairy:
:fairy_tone1:
:fairy_tone2:
:fairy_tone3:
:fairy_tone4:
:fairy_tone5:
:family:
:family_man_boy:
:family_man_boy_boy:
:family_man_girl:
:family_man_girl_boy:
:family_man_girl_girl:
:family_man_woman_boy:
:family_mmb:
:family_mmbb:
:family_mmg:
:family_mmgb:
:family_mmgg:
:family_mwbb:
:family_mwg:
:family_mwgb:
:family_mwgg:
:family_woman_boy:
:family_woman_boy_boy:
:family_woman_girl:
:family_woman_girl_boy:
:family_woman_girl_girl:
:family_wwb:
:family_wwbb:
:family_wwg:
:family_wwgb:
:family_wwgg:
:fearful:
:fingers_crossed:
:fingers_crossed_tone1:
:fingers_crossed_tone2:
:fingers_crossed_tone3:
:fingers_crossed_tone4:
:fingers_crossed_tone5:
:fist:
:fist_tone1:
:fist_tone2:
:fist_tone3:
:fist_tone4:
:fist_tone5:
:flushed:
:foot:
:foot_tone1:
:foot_tone2:
:foot_tone3:
:foot_tone4:
:foot_tone5:
:footprints:
:frowning2:
:frowning:
:genie:
:ghost:
:girl:
:girl_tone1:
:girl_tone2:
:girl_tone3:
:girl_tone4:
:girl_tone5:
:gloves:
:goggles:
:grimacing:
:grin:
:grinning:
:guard:
:guard_tone1:
:guard_tone2:
:guard_tone3:
:guard_tone4:
:guard_tone5:
:hand_splayed:
:hand_splayed_tone1:
:hand_splayed_tone2:
:hand_splayed_tone3:
:hand_splayed_tone4:
:hand_splayed_tone5:
:handbag:
:handshake:
:head_bandage:
:heart_eyes:
:heart_eyes_cat:
:helmet_with_cross:
:high_heel:
:hiking_boot:
:hot_face:
:hugging:
:hushed:
:imp:
:innocent:
:jack_o_lantern:
:japanese_goblin:
:japanese_ogre:
:jeans:
:joy:
:joy_cat:
:kimono:
:kiss:
:kiss_mm:
:kiss_woman_man:
:kiss_ww:
:kissing:
:kissing_cat:
:kissing_closed_eyes:
:kissing_heart:
:kissing_smiling_eyes:
:lab_coat:
:laughing:
:left_facing_fist:
:left_facing_fist_tone1:
:left_facing_fist_tone2:
:left_facing_fist_tone3:
:left_facing_fist_tone4:
:left_facing_fist_tone5:
:leg:
:leg_tone1:
:leg_tone2:
:leg_tone3:
:leg_tone4:
:leg_tone5:
:levitate:
:levitate_tone1:
:levitate_tone2:
:levitate_tone3:
:levitate_tone4:
:levitate_tone5:
:lips:
:lipstick:
:love_you_gesture:
:love_you_gesture_tone1:
:love_you_gesture_tone2:
:love_you_gesture_tone3:
:love_you_gesture_tone4:
:love_you_gesture_tone5:
:luggage:
:lying_face:
:mage:
:mage_tone1:
:mage_tone2:
:mage_tone3:
:mage_tone4:
:mage_tone5:
:man:
:man_artist:
:man_artist_tone1:
:man_artist_tone2:
:man_artist_tone3:
:man_artist_tone4:
:man_artist_tone5:
:man_astronaut:
:man_astronaut_tone1:
:man_astronaut_tone2:
:man_astronaut_tone3:
:man_astronaut_tone4:
:man_astronaut_tone5:
:man_bald:
:man_bald_tone1:
:man_bald_tone2:
:man_bald_tone3:
:man_bald_tone4:
:man_bald_tone5:
:man_bowing:
:man_bowing_tone1:
:man_bowing_tone2:
:man_bowing_tone3:
:man_bowing_tone4:
:man_bowing_tone5:
:man_construction_worker:
:man_construction_worker_tone1:
:man_construction_worker_tone2:
:man_construction_worker_tone3:
:man_construction_worker_tone4:
:man_construction_worker_tone5:
:man_cook:
:man_cook_tone1:
:man_cook_tone2:
:man_cook_tone3:
:man_cook_tone4:
:man_cook_tone5:
:man_curly_haired:
:man_curly_haired_tone1:
:man_curly_haired_tone2:
:man_curly_haired_tone3:
:man_curly_haired_tone4:
:man_curly_haired_tone5:
:man_dancing:
:man_dancing_tone1:
:man_dancing_tone2:
:man_dancing_tone3:
:man_dancing_tone4:
:man_dancing_tone5:
:man_detective:
:man_detective_tone1:
:man_detective_tone2:
:man_detective_tone3:
:man_detective_tone4:
:man_detective_tone5:
:man_elf:
:man_elf_tone1:
:man_elf_tone2:
:man_elf_tone3:
:man_elf_tone4:
:man_elf_tone5:
:man_facepalming:
:man_facepalming_tone1:
:man_facepalming_tone2:
:man_facepalming_tone3:
:man_facepalming_tone4:
:man_facepalming_tone5:
:man_factory_worker:
:man_factory_worker_tone1:
:man_factory_worker_tone2:
:man_factory_worker_tone3:
:man_factory_worker_tone4:
:man_factory_worker_tone5:
:man_fairy:
:man_fairy_tone1:
:man_fairy_tone2:
:man_fairy_tone3:
:man_fairy_tone4:
:man_fairy_tone5:
:man_farmer:
:man_farmer_tone1:
:man_farmer_tone2:
:man_farmer_tone3:
:man_farmer_tone4:
:man_farmer_tone5:
:man_firefighter:
:man_firefighter_tone1:
:man_firefighter_tone2:
:man_firefighter_tone3:
:man_firefighter_tone4:
:man_firefighter_tone5:
:man_frowning:
:man_frowning_tone1:
:man_frowning_tone2:
:man_frowning_tone3:
:man_frowning_tone4:
:man_frowning_tone5:
:man_genie:
:man_gesturing_no:
:man_gesturing_no_tone1:
:man_gesturing_no_tone2:
:man_gesturing_no_tone3:
:man_gesturing_no_tone4:
:man_gesturing_no_tone5:
:man_gesturing_ok:
:man_gesturing_ok_tone1:
:man_gesturing_ok_tone2:
:man_gesturing_ok_tone3:
:man_gesturing_ok_tone4:
:man_gesturing_ok_tone5:
:man_getting_face_massage:
:man_getting_face_massage_tone1:
:man_getting_face_massage_tone2:
:man_getting_face_massage_tone3:
:man_getting_face_massage_tone4:
:man_getting_face_massage_tone5:
:man_getting_haircut:
:man_getting_haircut_tone1:
:man_getting_haircut_tone2:
:man_getting_haircut_tone3:
:man_getting_haircut_tone4:
:man_getting_haircut_tone5:
:man_guard:
:man_guard_tone1:
:man_guard_tone2:
:man_guard_tone3:
:man_guard_tone4:
:man_guard_tone5:
:man_health_worker:
:man_health_worker_tone1:
:man_health_worker_tone2:
:man_health_worker_tone3:
:man_health_worker_tone4:
:man_health_worker_tone5:
:man_in_manual_wheelchair:
:man_in_manual_wheelchair_tone1:
:man_in_manual_wheelchair_tone2:
:man_in_manual_wheelchair_tone3:
:man_in_manual_wheelchair_tone4:
:man_in_manual_wheelchair_tone5:
:man_in_motorized_wheelchair:
:man_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone1:
:man_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone2:
:man_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone3:
:man_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone4:
:man_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone5:
:man_in_steamy_room:
:man_in_steamy_room_tone1:
:man_in_steamy_room_tone2:
:man_in_steamy_room_tone3:
:man_in_steamy_room_tone4:
:man_in_steamy_room_tone5:
:man_in_tuxedo:
:man_in_tuxedo_tone1:
:man_in_tuxedo_tone2:
:man_in_tuxedo_tone3:
:man_in_tuxedo_tone4:
:man_in_tuxedo_tone5:
:man_judge:
:man_judge_tone1:
:man_judge_tone2:
:man_judge_tone3:
:man_judge_tone4:
:man_judge_tone5:
:man_kneeling:
:man_kneeling_tone1:
:man_kneeling_tone2:
:man_kneeling_tone3:
:man_kneeling_tone4:
:man_kneeling_tone5:
:man_mage:
:man_mage_tone1:
:man_mage_tone2:
:man_mage_tone3:
:man_mage_tone4:
:man_mage_tone5:
:man_mechanic:
:man_mechanic_tone1:
:man_mechanic_tone2:
:man_mechanic_tone3:
:man_mechanic_tone4:
:man_mechanic_tone5:
:man_office_worker:
:man_office_worker_tone1:
:man_office_worker_tone2:
:man_office_worker_tone3:
:man_office_worker_tone4:
:man_office_worker_tone5:
:man_pilot:
:man_pilot_tone1:
:man_pilot_tone2:
:man_pilot_tone3:
:man_pilot_tone4:
:man_pilot_tone5:
:man_police_officer:
:man_police_officer_tone1:
:man_police_officer_tone2:
:man_police_officer_tone3:
:man_police_officer_tone4:
:man_police_officer_tone5:
:man_pouting:
:man_pouting_tone1:
:man_pouting_tone2:
:man_pouting_tone3:
:man_pouting_tone4:
:man_pouting_tone5:
:man_raising_hand:
:man_raising_hand_tone1:
:man_raising_hand_tone2:
:man_raising_hand_tone3:
:man_raising_hand_tone4:
:man_raising_hand_tone5:
:man_red_haired:
:man_red_haired_tone1:
:man_red_haired_tone2:
:man_red_haired_tone3:
:man_red_haired_tone4:
:man_red_haired_tone5:
:man_running:
:man_running_tone1:
:man_running_tone2:
:man_running_tone3:
:man_running_tone4:
:man_running_tone5:
:man_scientist:
:man_scientist_tone1:
:man_scientist_tone2:
:man_scientist_tone3:
:man_scientist_tone4:
:man_scientist_tone5:
:man_shrugging:
:man_shrugging_tone1:
:man_shrugging_tone2:
:man_shrugging_tone3:
:man_shrugging_tone4:
:man_shrugging_tone5:
:man_singer:
:man_singer_tone1:
:man_singer_tone2:
:man_singer_tone3:
:man_singer_tone4:
:man_singer_tone5:
:man_standing:
:man_standing_tone1:
:man_standing_tone2:
:man_standing_tone3:
:man_standing_tone4:
:man_standing_tone5:
:man_student:
:man_student_tone1:
:man_student_tone2:
:man_student_tone3:
:man_student_tone4:
:man_student_tone5:
:man_superhero:
:man_superhero_tone1:
:man_superhero_tone2:
:man_superhero_tone3:
:man_superhero_tone4:
:man_superhero_tone5:
:man_supervillain:
:man_supervillain_tone1:
:man_supervillain_tone2:
:man_supervillain_tone3:
:man_supervillain_tone4:
:man_supervillain_tone5:
:man_teacher:
:man_teacher_tone1:
:man_teacher_tone2:
:man_teacher_tone3:
:man_teacher_tone4:
:man_teacher_tone5:
:man_technologist:
:man_technologist_tone1:
:man_technologist_tone2:
:man_technologist_tone3:
:man_technologist_tone4:
:man_technologist_tone5:
:man_tipping_hand:
:man_tipping_hand_tone1:
:man_tipping_hand_tone2:
:man_tipping_hand_tone3:
:man_tipping_hand_tone4:
:man_tipping_hand_tone5:
:man_tone1:
:man_tone2:
:man_tone3:
:man_tone4:
:man_tone5:
:man_vampire:
:man_vampire_tone1:
:man_vampire_tone2:
:man_vampire_tone3:
:man_vampire_tone4:
:man_vampire_tone5:
:man_walking:
:man_walking_tone1:
:man_walking_tone2:
:man_walking_tone3:
:man_walking_tone4:
:man_walking_tone5:
:man_wearing_turban:
:man_wearing_turban_tone1:
:man_wearing_turban_tone2:
:man_wearing_turban_tone3:
:man_wearing_turban_tone4:
:man_wearing_turban_tone5:
:man_white_haired:
:man_white_haired_tone1:
:man_white_haired_tone2:
:man_white_haired_tone3:
:man_white_haired_tone4:
:man_white_haired_tone5:
:man_with_chinese_cap:
:man_with_chinese_cap_tone1:
:man_with_chinese_cap_tone2:
:man_with_chinese_cap_tone3:
:man_with_chinese_cap_tone4:
:man_with_chinese_cap_tone5:
:man_with_probing_cane:
:man_with_probing_cane_tone1:
:man_with_probing_cane_tone2:
:man_with_probing_cane_tone3:
:man_with_probing_cane_tone4:
:man_with_probing_cane_tone5:
:man_zombie:
:mans_shoe:
:mask:
:mechanical_arm:
:mechanical_leg:
:men_holding_hands_tone1:
:men_holding_hands_tone2:
:men_holding_hands_tone2_tone1:
:men_holding_hands_tone3:
:men_holding_hands_tone3_tone1:
:men_holding_hands_tone3_tone2:
:men_holding_hands_tone4:
:men_holding_hands_tone4_tone1:
:men_holding_hands_tone4_tone2:
:men_holding_hands_tone4_tone3:
:men_holding_hands_tone5:
:men_holding_hands_tone5_tone1:
:men_holding_hands_tone5_tone2:
:men_holding_hands_tone5_tone3:
:men_holding_hands_tone5_tone4:
:men_with_bunny_ears_partying:
:mermaid:
:mermaid_tone1:
:mermaid_tone2:
:mermaid_tone3:
:mermaid_tone4:
:mermaid_tone5:
:merman:
:merman_tone1:
:merman_tone2:
:merman_tone3:
:merman_tone4:
:merman_tone5:
:merperson:
:merperson_tone1:
:merperson_tone2:
:merperson_tone3:
:merperson_tone4:
:merperson_tone5:
:metal:
:metal_tone1:
:metal_tone2:
:metal_tone3:
:metal_tone4:
:metal_tone5:
:middle_finger:
:middle_finger_tone1:
:middle_finger_tone2:
:middle_finger_tone3:
:middle_finger_tone4:
:middle_finger_tone5:
:money_mouth:
:mortar_board:
:mrs_claus:
:mrs_claus_tone1:
:mrs_claus_tone2:
:mrs_claus_tone3:
:mrs_claus_tone4:
:mrs_claus_tone5:
:muscle:
:muscle_tone1:
:muscle_tone2:
:muscle_tone3:
:muscle_tone4:
:muscle_tone5:
:nail_care:
:nail_care_tone1:
:nail_care_tone2:
:nail_care_tone3:
:nail_care_tone4:
:nail_care_tone5:
:nauseated_face:
:necktie:
:nerd:
:neutral_face:
:no_mouth:
:nose:
:nose_tone1:
:nose_tone2:
:nose_tone3:
:nose_tone4:
:nose_tone5:
:ok_hand:
:ok_hand_tone1:
:ok_hand_tone2:
:ok_hand_tone3:
:ok_hand_tone4:
:ok_hand_tone5:
:older_adult:
:older_adult_tone1:
:older_adult_tone2:
:older_adult_tone3:
:older_adult_tone4:
:older_adult_tone5:
:older_man:
:older_man_tone1:
:older_man_tone2:
:older_man_tone3:
:older_man_tone4:
:older_man_tone5:
:older_woman:
:older_woman_tone1:
:older_woman_tone2:
:older_woman_tone3:
:older_woman_tone4:
:older_woman_tone5:
:one_piece_swimsuit:
:open_hands:
:open_hands_tone1:
:open_hands_tone2:
:open_hands_tone3:
:open_hands_tone4:
:open_hands_tone5:
:open_mouth:
:palms_up_together:
:palms_up_together_tone1:
:palms_up_together_tone2:
:palms_up_together_tone3:
:palms_up_together_tone4:
:palms_up_together_tone5:
:partying_face:
:pensive:
:people_holding_hands:
:people_holding_hands_tone1:
:people_holding_hands_tone2:
:people_holding_hands_tone2_tone1:
:people_holding_hands_tone3:
:people_holding_hands_tone3_tone1:
:people_holding_hands_tone3_tone2:
:people_holding_hands_tone4:
:people_holding_hands_tone4_tone1:
:people_holding_hands_tone4_tone2:
:people_holding_hands_tone4_tone3:
:people_holding_hands_tone5:
:people_holding_hands_tone5_tone1:
:people_holding_hands_tone5_tone2:
:people_holding_hands_tone5_tone3:
:people_holding_hands_tone5_tone4:
:people_with_bunny_ears_partying:
:persevere:
:person_bowing:
:person_bowing_tone1:
:person_bowing_tone2:
:person_bowing_tone3:
:person_bowing_tone4:
:person_bowing_tone5:
:person_facepalming:
:person_facepalming_tone1:
:person_facepalming_tone2:
:person_facepalming_tone3:
:person_facepalming_tone4:
:person_facepalming_tone5:
:person_frowning:
:person_frowning_tone1:
:person_frowning_tone2:
:person_frowning_tone3:
:person_frowning_tone4:
:person_frowning_tone5:
:person_gesturing_no:
:person_gesturing_no_tone1:
:person_gesturing_no_tone2:
:person_gesturing_no_tone3:
:person_gesturing_no_tone4:
:person_gesturing_no_tone5:
:person_gesturing_ok:
:person_gesturing_ok_tone1:
:person_gesturing_ok_tone2:
:person_gesturing_ok_tone3:
:person_gesturing_ok_tone4:
:person_gesturing_ok_tone5:
:person_getting_haircut:
:person_getting_haircut_tone1:
:person_getting_haircut_tone2:
:person_getting_haircut_tone3:
:person_getting_haircut_tone4:
:person_getting_haircut_tone5:
:person_getting_massage:
:person_getting_massage_tone1:
:person_getting_massage_tone2:
:person_getting_massage_tone3:
:person_getting_massage_tone4:
:person_getting_massage_tone5:
:person_in_steamy_room:
:person_in_steamy_room_tone1:
:person_in_steamy_room_tone2:
:person_in_steamy_room_tone3:
:person_in_steamy_room_tone4:
:person_in_steamy_room_tone5:
:person_kneeling:
:person_kneeling_tone1:
:person_kneeling_tone2:
:person_kneeling_tone3:
:person_kneeling_tone4:
:person_kneeling_tone5:
:person_pouting:
:person_pouting_tone1:
:person_pouting_tone2:
:person_pouting_tone3:
:person_pouting_tone4:
:person_pouting_tone5:
:person_raising_hand:
:person_raising_hand_tone1:
:person_raising_hand_tone2:
:person_raising_hand_tone3:
:person_raising_hand_tone4:
:person_raising_hand_tone5:
:person_running:
:person_running_tone1:
:person_running_tone2:
:person_running_tone3:
:person_running_tone4:
:person_running_tone5:
:person_shrugging:
:person_shrugging_tone1:
:person_shrugging_tone2:
:person_shrugging_tone3:
:person_shrugging_tone4:
:person_shrugging_tone5:
:person_standing:
:person_standing_tone1:
:person_standing_tone2:
:person_standing_tone3:
:person_standing_tone4:
:person_standing_tone5:
:person_tipping_hand:
:person_tipping_hand_tone1:
:person_tipping_hand_tone2:
:person_tipping_hand_tone3:
:person_tipping_hand_tone4:
:person_tipping_hand_tone5:
:person_walking:
:person_walking_tone1:
:person_walking_tone2:
:person_walking_tone3:
:person_walking_tone4:
:person_walking_tone5:
:person_wearing_turban:
:person_wearing_turban_tone1:
:person_wearing_turban_tone2:
:person_wearing_turban_tone3:
:person_wearing_turban_tone4:
:person_wearing_turban_tone5:
:pinching_hand:
:pinching_hand_tone1:
:pinching_hand_tone2:
:pinching_hand_tone3:
:pinching_hand_tone4:
:pinching_hand_tone5:
:pleading_face:
:point_down:
:point_down_tone1:
:point_down_tone2:
:point_down_tone3:
:point_down_tone4:
:point_down_tone5:
:point_left:
:point_left_tone1:
:point_left_tone2:
:point_left_tone3:
:point_left_tone4:
:point_left_tone5:
:point_right:
:point_right_tone1:
:point_right_tone2:
:point_right_tone3:
:point_right_tone4:
:point_right_tone5:
:point_up:
:point_up_2:
:point_up_2_tone1:
:point_up_2_tone2:
:point_up_2_tone3:
:point_up_2_tone4:
:point_up_2_tone5:
:point_up_tone1:
:point_up_tone2:
:point_up_tone3:
:point_up_tone4:
:point_up_tone5:
:police_officer:
:police_officer_tone1:
:police_officer_tone2:
:police_officer_tone3:
:police_officer_tone4:
:police_officer_tone5:
:poop:
:pouch:
:pouting_cat:
:pray:
:pray_tone1:
:pray_tone2:
:pray_tone3:
:pray_tone4:
:pray_tone5:
:pregnant_woman:
:pregnant_woman_tone1:
:pregnant_woman_tone2:
:pregnant_woman_tone3:
:pregnant_woman_tone4:
:pregnant_woman_tone5:
:prince:
:prince_tone1:
:prince_tone2:
:prince_tone3:
:prince_tone4:
:prince_tone5:
:princess:
:princess_tone1:
:princess_tone2:
:princess_tone3:
:princess_tone4:
:princess_tone5:
:punch:
:punch_tone1:
:punch_tone2:
:punch_tone3:
:punch_tone4:
:punch_tone5:
:purse:
:rage:
:raised_back_of_hand:
:raised_back_of_hand_tone1:
:raised_back_of_hand_tone2:
:raised_back_of_hand_tone3:
:raised_back_of_hand_tone4:
:raised_back_of_hand_tone5:
:raised_hand:
:raised_hand_tone1:
:raised_hand_tone2:
:raised_hand_tone3:
:raised_hand_tone4:
:raised_hand_tone5:
:raised_hands:
:raised_hands_tone1:
:raised_hands_tone2:
:raised_hands_tone3:
:raised_hands_tone4:
:raised_hands_tone5:
:red_haired:
:relaxed:
:relieved:
:right_facing_fist:
:right_facing_fist_tone1:
:right_facing_fist_tone2:
:right_facing_fist_tone3:
:right_facing_fist_tone4:
:right_facing_fist_tone5:
:ring:
:robot:
:rofl:
:rolling_eyes:
:safety_vest:
:sandal:
:santa:
:santa_tone1:
:santa_tone2:
:santa_tone3:
:santa_tone4:
:santa_tone5:
:sari:
:scarf:
:school_satchel:
:scream:
:scream_cat:
:selfie:
:selfie_tone1:
:selfie_tone2:
:selfie_tone3:
:selfie_tone4:
:selfie_tone5:
:shirt:
:shorts:
:shushing_face:
:skull:
:skull_crossbones:
:sleeping:
:sleepy:
:slight_frown:
:slight_smile:
:smile:
:smile_cat:
:smiley:
:smiley_cat:
:smiling_face_with_3_hearts:
:smiling_imp:
:smirk:
:smirk_cat:
:sneezing_face:
:sob:
:socks:
:space_invader:
:speaking_head:
:star_struck:
:stuck_out_tongue:
:stuck_out_tongue_closed_eyes:
:stuck_out_tongue_winking_eye:
:sunglasses:
:superhero:
:superhero_tone1:
:superhero_tone2:
:superhero_tone3:
:superhero_tone4:
:superhero_tone5:
:supervillain:
:supervillain_tone1:
:supervillain_tone2:
:supervillain_tone3:
:supervillain_tone4:
:supervillain_tone5:
:sweat:
:sweat_smile:
:thermometer_face:
:thinking:
:thread:
:thumbsdown:
:thumbsdown_tone1:
:thumbsdown_tone2:
:thumbsdown_tone3:
:thumbsdown_tone4:
:thumbsdown_tone5:
:thumbsup:
:thumbsup_tone1:
:thumbsup_tone2:
:thumbsup_tone3:
:thumbsup_tone4:
:thumbsup_tone5:
:tired_face:
:tongue:
:tooth:
:tophat:
:triumph:
:two_men_holding_hands:
:two_women_holding_hands:
:unamused:
:upside_down:
:v:
:v_tone1:
:v_tone2:
:v_tone3:
:v_tone4:
:v_tone5:
:vampire:
:vampire_tone1:
:vampire_tone2:
:vampire_tone3:
:vampire_tone4:
:vampire_tone5:
:vulcan:
:vulcan_tone1:
:vulcan_tone2:
:vulcan_tone3:
:vulcan_tone4:
:vulcan_tone5:
:wave:
:wave_tone1:
:wave_tone2:
:wave_tone3:
:wave_tone4:
:wave_tone5:
:weary:
:white_haired:
:wink:
:woman:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone1:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone1_tone2:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone1_tone3:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone1_tone4:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone1_tone5:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone2:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone2_tone1:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone2_tone3:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone2_tone4:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone2_tone5:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone3:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone3_tone1:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone3_tone2:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone3_tone4:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone3_tone5:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone4:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone4_tone1:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone4_tone2:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone4_tone3:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone4_tone5:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone5:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone5_tone1:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone5_tone2:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone5_tone3:
:woman_and_man_holding_hands_tone5_tone4:
:woman_artist:
:woman_artist_tone1:
:woman_artist_tone2:
:woman_artist_tone3:
:woman_artist_tone4:
:woman_artist_tone5:
:woman_astronaut:
:woman_astronaut_tone1:
:woman_astronaut_tone2:
:woman_astronaut_tone3:
:woman_astronaut_tone4:
:woman_astronaut_tone5:
:woman_bald:
:woman_bald_tone1:
:woman_bald_tone2:
:woman_bald_tone3:
:woman_bald_tone4:
:woman_bald_tone5:
:woman_bowing:
:woman_bowing_tone1:
:woman_bowing_tone2:
:woman_bowing_tone3:
:woman_bowing_tone4:
:woman_bowing_tone5:
:woman_construction_worker:
:woman_construction_worker_tone1:
:woman_construction_worker_tone2:
:woman_construction_worker_tone3:
:woman_construction_worker_tone4:
:woman_construction_worker_tone5:
:woman_cook:
:woman_cook_tone1:
:woman_cook_tone2:
:woman_cook_tone3:
:woman_cook_tone4:
:woman_cook_tone5:
:woman_curly_haired:
:woman_curly_haired_tone1:
:woman_curly_haired_tone2:
:woman_curly_haired_tone3:
:woman_curly_haired_tone4:
:woman_curly_haired_tone5:
:woman_detective:
:woman_detective_tone1:
:woman_detective_tone2:
:woman_detective_tone3:
:woman_detective_tone4:
:woman_detective_tone5:
:woman_elf:
:woman_elf_tone1:
:woman_elf_tone2:
:woman_elf_tone3:
:woman_elf_tone4:
:woman_elf_tone5:
:woman_facepalming:
:woman_facepalming_tone1:
:woman_facepalming_tone2:
:woman_facepalming_tone3:
:woman_facepalming_tone4:
:woman_facepalming_tone5:
:woman_factory_worker:
:woman_factory_worker_tone1:
:woman_factory_worker_tone2:
:woman_factory_worker_tone3:
:woman_factory_worker_tone4:
:woman_factory_worker_tone5:
:woman_fairy:
:woman_fairy_tone1:
:woman_fairy_tone2:
:woman_fairy_tone3:
:woman_fairy_tone4:
:woman_fairy_tone5:
:woman_farmer:
:woman_farmer_tone1:
:woman_farmer_tone2:
:woman_farmer_tone3:
:woman_farmer_tone4:
:woman_farmer_tone5:
:woman_firefighter:
:woman_firefighter_tone1:
:woman_firefighter_tone2:
:woman_firefighter_tone3:
:woman_firefighter_tone4:
:woman_firefighter_tone5:
:woman_frowning:
:woman_frowning_tone1:
:woman_frowning_tone2:
:woman_frowning_tone3:
:woman_frowning_tone4:
:woman_frowning_tone5:
:woman_genie:
:woman_gesturing_no:
:woman_gesturing_no_tone1:
:woman_gesturing_no_tone2:
:woman_gesturing_no_tone3:
:woman_gesturing_no_tone4:
:woman_gesturing_no_tone5:
:woman_gesturing_ok:
:woman_gesturing_ok_tone1:
:woman_gesturing_ok_tone2:
:woman_gesturing_ok_tone3:
:woman_gesturing_ok_tone4:
:woman_gesturing_ok_tone5:
:woman_getting_face_massage:
:woman_getting_face_massage_tone1:
:woman_getting_face_massage_tone2:
:woman_getting_face_massage_tone3:
:woman_getting_face_massage_tone4:
:woman_getting_face_massage_tone5:
:woman_getting_haircut:
:woman_getting_haircut_tone1:
:woman_getting_haircut_tone2:
:woman_getting_haircut_tone3:
:woman_getting_haircut_tone4:
:woman_getting_haircut_tone5:
:woman_guard:
:woman_guard_tone1:
:woman_guard_tone2:
:woman_guard_tone3:
:woman_guard_tone4:
:woman_guard_tone5:
:woman_health_worker:
:woman_health_worker_tone1:
:woman_health_worker_tone2:
:woman_health_worker_tone3:
:woman_health_worker_tone4:
:woman_health_worker_tone5:
:woman_in_manual_wheelchair:
:woman_in_manual_wheelchair_tone1:
:woman_in_manual_wheelchair_tone2:
:woman_in_manual_wheelchair_tone3:
:woman_in_manual_wheelchair_tone4:
:woman_in_manual_wheelchair_tone5:
:woman_in_motorized_wheelchair:
:woman_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone1:
:woman_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone2:
:woman_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone3:
:woman_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone4:
:woman_in_motorized_wheelchair_tone5:
:woman_in_steamy_room:
:woman_in_steamy_room_tone1:
:woman_in_steamy_room_tone2:
:woman_in_steamy_room_tone3:
:woman_in_steamy_room_tone4:
:woman_in_steamy_room_tone5:
:woman_judge:
:woman_judge_tone1:
:woman_judge_tone2:
:woman_judge_tone3:
:woman_judge_tone4:
:woman_judge_tone5:
:woman_kneeling:
:woman_kneeling_tone1:
:woman_kneeling_tone2:
:woman_kneeling_tone3:
:woman_kneeling_tone4:
:woman_kneeling_tone5:
:woman_mage:
:woman_mage_tone1:
:woman_mage_tone2:
:woman_mage_tone3:
:woman_mage_tone4:
:woman_mage_tone5:
:woman_mechanic:
:woman_mechanic_tone1:
:woman_mechanic_tone2:
:woman_mechanic_tone3:
:woman_mechanic_tone4:
:woman_mechanic_tone5:
:woman_office_worker:
:woman_office_worker_tone1:
:woman_office_worker_tone2:
:woman_office_worker_tone3:
:woman_office_worker_tone4:
:woman_office_worker_tone5:
:woman_pilot:
:woman_pilot_tone1:
:woman_pilot_tone2:
:woman_pilot_tone3:
:woman_pilot_tone4:
:woman_pilot_tone5:
:woman_police_officer:
:woman_police_officer_tone1:
:woman_police_officer_tone2:
:woman_police_officer_tone3:
:woman_police_officer_tone4:
:woman_police_officer_tone5:
:woman_pouting:
:woman_pouting_tone1:
:woman_pouting_tone2:
:woman_pouting_tone3:
:woman_pouting_tone4:
:woman_pouting_tone5:
:woman_raising_hand:
:woman_raising_hand_tone1:
:woman_raising_hand_tone2:
:woman_raising_hand_tone3:
:woman_raising_hand_tone4:
:woman_raising_hand_tone5:
:woman_red_haired:
:woman_red_haired_tone1:
:woman_red_haired_tone2:
:woman_red_haired_tone3:
:woman_red_haired_tone4:
:woman_red_haired_tone5:
:woman_running:
:woman_running_tone1:
:woman_running_tone2:
:woman_running_tone3:
:woman_running_tone4:
:woman_running_tone5:
:woman_scientist:
:woman_scientist_tone1:
:woman_scientist_tone2:
:woman_scientist_tone3:
:woman_scientist_tone4:
:woman_scientist_tone5:
:woman_shrugging:
:woman_shrugging_tone1:
:woman_shrugging_tone2:
:woman_shrugging_tone3:
:woman_shrugging_tone4:
:woman_shrugging_tone5:
:woman_singer:
:woman_singer_tone1:
:woman_singer_tone2:
:woman_singer_tone3:
:woman_singer_tone4:
:woman_singer_tone5:
:woman_standing:
:woman_standing_tone1:
:woman_standing_tone2:
:woman_standing_tone3:
:woman_standing_tone4:
:woman_standing_tone5:
:woman_student:
:woman_student_tone1:
:woman_student_tone2:
:woman_student_tone3:
:woman_student_tone4:
:woman_student_tone5:
:woman_superhero:
:woman_superhero_tone1:
:woman_superhero_tone2:
:woman_superhero_tone3:
:woman_superhero_tone4:
:woman_superhero_tone5:
:woman_supervillain:
:woman_supervillain_tone1:
:woman_supervillain_tone2:
:woman_supervillain_tone3:
:woman_supervillain_tone4:
:woman_supervillain_tone5:
:woman_teacher:
:woman_teacher_tone1:
:woman_teacher_tone2:
:woman_teacher_tone3:
:woman_teacher_tone4:
:woman_teacher_tone5:
:woman_technologist:
:woman_technologist_tone1:
:woman_technologist_tone2:
:woman_technologist_tone3:
:woman_technologist_tone4:
:woman_technologist_tone5:
:woman_tipping_hand:
:woman_tipping_hand_tone1:
:woman_tipping_hand_tone2:
:woman_tipping_hand_tone3:
:woman_tipping_hand_tone4:
:woman_tipping_hand_tone5:
:woman_tone1:
:woman_tone2:
:woman_tone3:
:woman_tone4:
:woman_tone5:
:woman_vampire:
:woman_vampire_tone1:
:woman_vampire_tone2:
:woman_vampire_tone3:
:woman_vampire_tone4:
:woman_vampire_tone5:
:woman_walking:
:woman_walking_tone1:
:woman_walking_tone2:
:woman_walking_tone3:
:woman_walking_tone4:
:woman_walking_tone5:
:woman_wearing_turban:
:woman_wearing_turban_tone1:
:woman_wearing_turban_tone2:
:woman_wearing_turban_tone3:
:woman_wearing_turban_tone4:
:woman_wearing_turban_tone5:
:woman_white_haired:
:woman_white_haired_tone1:
:woman_white_haired_tone2:
:woman_white_haired_tone3:
:woman_white_haired_tone4:
:woman_white_haired_tone5:
:woman_with_headscarf:
:woman_with_headscarf_tone1:
:woman_with_headscarf_tone2:
:woman_with_headscarf_tone3:
:woman_with_headscarf_tone4:
:woman_with_headscarf_tone5:
:woman_with_probing_cane:
:woman_with_probing_cane_tone1:
:woman_with_probing_cane_tone2:
:woman_with_probing_cane_tone3:
:woman_with_probing_cane_tone4:
:woman_with_probing_cane_tone5:
:woman_zombie:
:womans_clothes:
:womans_flat_shoe:
:womans_hat:
:women_holding_hands_tone1:
:women_holding_hands_tone2:
:women_holding_hands_tone2_tone1:
:women_holding_hands_tone3:
:women_holding_hands_tone3_tone1:
:women_holding_hands_tone3_tone2:
:women_holding_hands_tone4:
:women_holding_hands_tone4_tone1:
:women_holding_hands_tone4_tone2:
:women_holding_hands_tone4_tone3:
:women_holding_hands_tone5:
:women_holding_hands_tone5_tone1:
:women_holding_hands_tone5_tone2:
:women_holding_hands_tone5_tone3:
:women_holding_hands_tone5_tone4:
:women_with_bunny_ears_partying:
:woozy_face:
:worried:
:writing_hand:
:writing_hand_tone1:
:writing_hand_tone2:
:writing_hand_tone3:
:writing_hand_tone4:
:writing_hand_tone5:
:yarn:
:yawning_face:
:yum:
:zany_face:
:zipper_mouth:
:zombie:
:regional_indicator_a:
:regional_indicator_b:
:regional_indicator_c:
:regional_indicator_d:
:regional_indicator_e:
:regional_indicator_f:
:regional_indicator_g:
:regional_indicator_h:
:regional_indicator_i:
:regional_indicator_j:
:regional_indicator_k:
:regional_indicator_l:
:regional_indicator_m:
:regional_indicator_n:
:regional_indicator_o:
:regional_indicator_p:
:regional_indicator_q:
:regional_indicator_r:
:regional_indicator_s:
:regional_indicator_t:
:regional_indicator_u:
:regional_indicator_v:
:regional_indicator_w:
:regional_indicator_x:
:regional_indicator_y:
:regional_indicator_z:
:100:
:1234:
:a:
:ab:
:abc:
:abcd:
:accept:
:anger:
:anger_right:
:aquarius:
:aries:
:arrow_backward:
:arrow_double_down:
:arrow_double_up:
:arrow_down:
:arrow_down_small:
:arrow_forward:
:arrow_heading_down:
:arrow_heading_up:
:arrow_left:
:arrow_lower_left:
:arrow_lower_right:
:arrow_right:
:arrow_right_hook:
:arrow_up:
:arrow_up_down:
:arrow_up_small:
:arrow_upper_left:
:arrow_upper_right:
:arrows_clockwise:
:arrows_counterclockwise:
:asterisk:
:asterisk_symbol:
:atm:
:atom:
:b:
:baby_symbol:
:back:
:baggage_claim:
:ballot_box_with_check:
:bangbang:
:beginner:
:bell:
:biohazard:
:black_circle:
:black_heart:
:black_joker:
:black_large_square:
:black_medium_small_square:
:black_medium_square:
:black_small_square:
:black_square_button:
:blue_circle:
:blue_heart:
:blue_square:
:broken_heart:
:brown_circle:
:brown_heart:
:brown_square:
:cancer:
:capital_abcd:
:capricorn:
:chart:
:children_crossing:
:cinema:
:cl:
:clock1030:
:clock10:
:clock1130:
:clock11:
:clock1230:
:clock12:
:clock130:
:clock1:
:clock230:
:clock2:
:clock330:
:clock3:
:clock430:
:clock4:
:clock530:
:clock5:
:clock630:
:clock6:
:clock730:
:clock7:
:clock830:
:clock8:
:clock930:
:clock9:
:clubs:
:congratulations:
:cool:
:copyright:
:cross:
:cupid:
:curly_loop:
:currency_exchange:
:customs:
:cyclone:
:diamond_shape_with_a_dot_inside:
:diamonds:
:digit_eight:
:digit_five:
:digit_four:
:digit_nine:
:digit_one:
:digit_seven:
:digit_six:
:digit_three:
:digit_two:
:digit_zero:
:do_not_litter:
:eight:
:eight_pointed_black_star:
:eight_spoked_asterisk:
:eject:
:end:
:exclamation:
:eye_in_speech_bubble:
:fast_forward:
:female_sign:
:five:
:fleur-de-lis:
:flower_playing_cards:
:four:
:free:
:gemini:
:gift_heart:
:globe_with_meridians:
:green_circle:
:green_heart:
:green_square:
:grey_exclamation:
:grey_question:
:hash:
:heart:
:heart_decoration:
:heart_exclamation:
:heartbeat:
:heartpulse:
:hearts:
:heavy_check_mark:
:heavy_division_sign:
:heavy_dollar_sign:
:heavy_minus_sign:
:heavy_multiplication_x:
:heavy_plus_sign:
:high_brightness:
:hotsprings:
:id:
:ideograph_advantage:
:infinity:
:information_source:
:interrobang:
:keycap_ten:
:koko:
:large_blue_diamond:
:large_orange_diamond:
:left_luggage:
:left_right_arrow:
:leftwards_arrow_with_hook:
:leo:
:libra:
:loop:
:loud_sound:
:loudspeaker:
:low_brightness:
:m:
:mahjong:
:male_sign:
:medical_symbol:
:mega:
:menorah:
:mens:
:mobile_phone_off:
:musical_note:
:mute:
:name_badge:
:negative_squared_cross_mark:
:new:
:ng:
:nine:
:no_bell:
:no_bicycles:
:no_entry:
:no_entry_sign:
:no_mobile_phones:
:no_pedestrians:
:no_smoking:
:non-potable_water:
:notes:
:o2:
:o:
:octagonal_sign:
:ok:
:om_symbol:
:on:
:one:
:ophiuchus:
:orange_circle:
:orange_heart:
:orange_square:
:orthodox_cross:
:parking:
:part_alternation_mark:
:passport_control:
:pause_button:
:peace:
:pisces:
:place_of_worship:
:play_pause:
:pound_symbol:
:purple_circle:
:purple_heart:
:purple_square:
:put_litter_in_its_place:
:question:
:radio_button:
:radioactive:
:record_button:
:recycle:
:red_circle:
:red_square:
:registered:
:repeat:
:repeat_one:
:restroom:
:revolving_hearts:
:rewind:
:sa:
:sagittarius:
:scorpius:
:secret:
:seven:
:signal_strength:
:six:
:six_pointed_star:
:small_blue_diamond:
:small_orange_diamond:
:small_red_triangle:
:small_red_triangle_down:
:soon:
:sos:
:sound:
:spades:
:sparkle:
:sparkling_heart:
:speaker:
:speech_balloon:
:speech_left:
:star_and_crescent:
:star_of_david:
:stop_button:
:symbols:
:taurus:
:thought_balloon:
:three:
:tm:
:top:
:track_next:
:track_previous:
:trident:
:twisted_rightwards_arrows:
:two:
:two_hearts:
:u5272:
:u5408:
:u55b6:
:u6307:
:u6708:
:u6709:
:u6e80:
:u7121:
:u7533:
:u7981:
:u7a7a:
:underage:
:up:
:vibration_mode:
:virgo:
:vs:
:warning:
:wavy_dash:
:wc:
:wheel_of_dharma:
:wheelchair:
:white_check_mark:
:white_circle:
:white_flower:
:white_heart:
:white_large_square:
:white_medium_small_square:
:white_medium_square:
:white_small_square:
:white_square_button:
:womens:
:x:
:yellow_circle:
:yellow_heart:
:yellow_square:
:yin_yang:
:zero:
:zzz:
:aerial_tramway:
:airplane:
:airplane_arriving:
:airplane_departure:
:airplane_small:
:ambulance:
:anchor:
:articulated_lorry:
:auto_rickshaw:
:bank:
:beach:
:beach_umbrella:
:bike:
:blue_car:
:bridge_at_night:
:bullettrain_front:
:bullettrain_side:
:bus:
:busstop:
:camping:
:canoe:
:carousel_horse:
:church:
:city_dusk:
:city_sunset:
:cityscape:
:classical_building:
:construction:
:construction_site:
:convenience_store:
:cruise_ship:
:department_store:
:desert:
:european_castle:
:european_post_office:
:factory:
:ferris_wheel:
:ferry:
:fire_engine:
:fireworks:
:flying_saucer:
:foggy:
:fountain:
:fuelpump:
:helicopter:
:hindu_temple:
:homes:
:hospital:
:hotel:
:house:
:house_abandoned:
:house_with_garden:
:island:
:japan:
:japanese_castle:
:kaaba:
:light_rail:
:love_hotel:
:manual_wheelchair:
:map:
:metro:
:milky_way:
:minibus:
:monorail:
:mosque:
:motor_scooter:
:motorboat:
:motorcycle:
:motorized_wheelchair:
:motorway:
:mount_fuji:
:mountain:
:mountain_cableway:
:mountain_railway:
:mountain_snow:
:moyai:
:night_with_stars:
:office:
:oncoming_automobile:
:oncoming_bus:
:oncoming_police_car:
:oncoming_taxi:
:park:
:police_car:
:post_office:
:race_car:
:railway_car:
:railway_track:
:red_car:
:rice_scene:
:rocket:
:roller_coaster:
:rotating_light:
:sailboat:
:satellite_orbital:
:school:
:scooter:
:seat:
:shinto_shrine:
:ship:
:sparkler:
:speedboat:
:stadium:
:stars:
:station:
:statue_of_liberty:
:steam_locomotive:
:sunrise:
:sunrise_over_mountains:
:suspension_railway:
:synagogue:
:taxi:
:tent:
:tokyo_tower:
:tractor:
:traffic_light:
:train2:
:train:
:tram:
:trolleybus:
:truck:
:vertical_traffic_light:
:volcano:
:wedding:
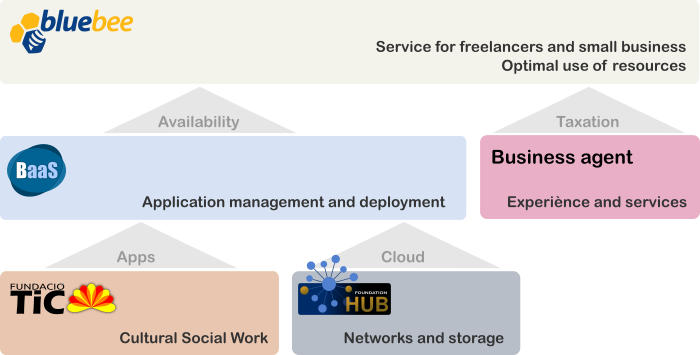
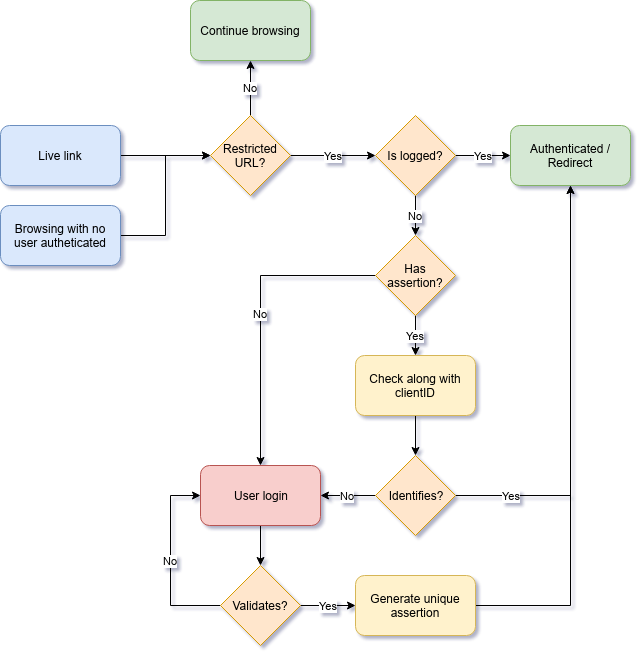
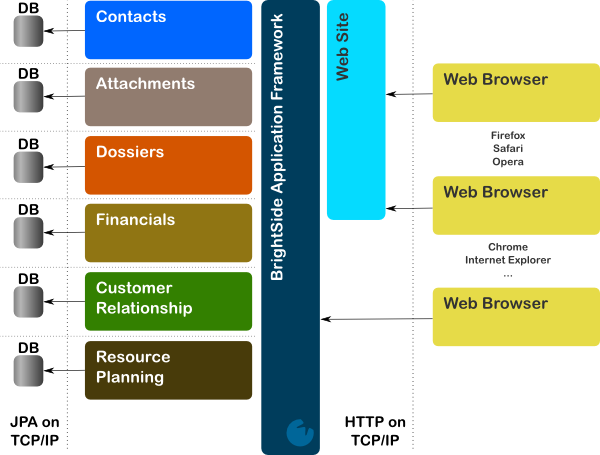
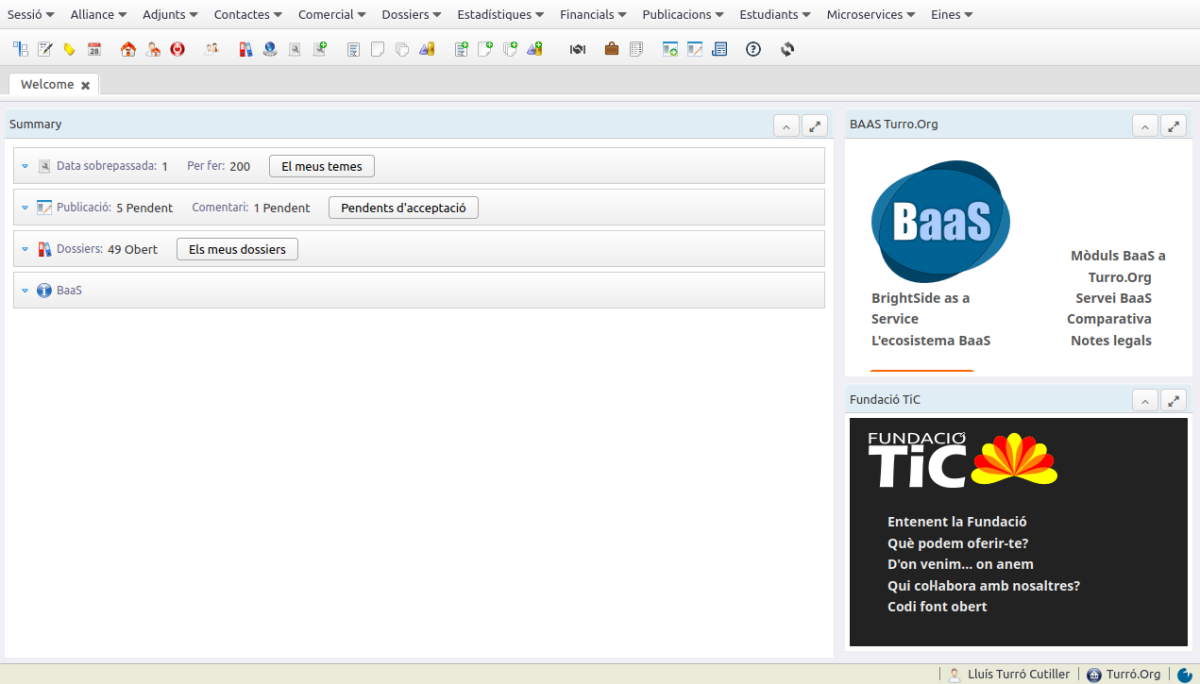

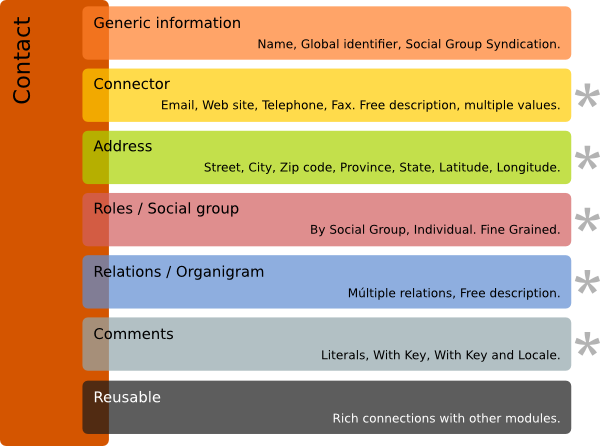
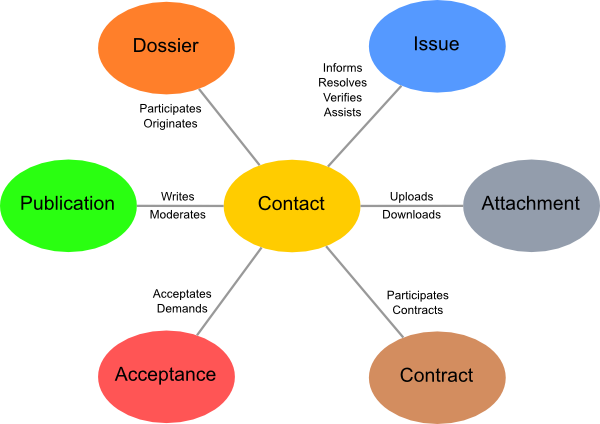

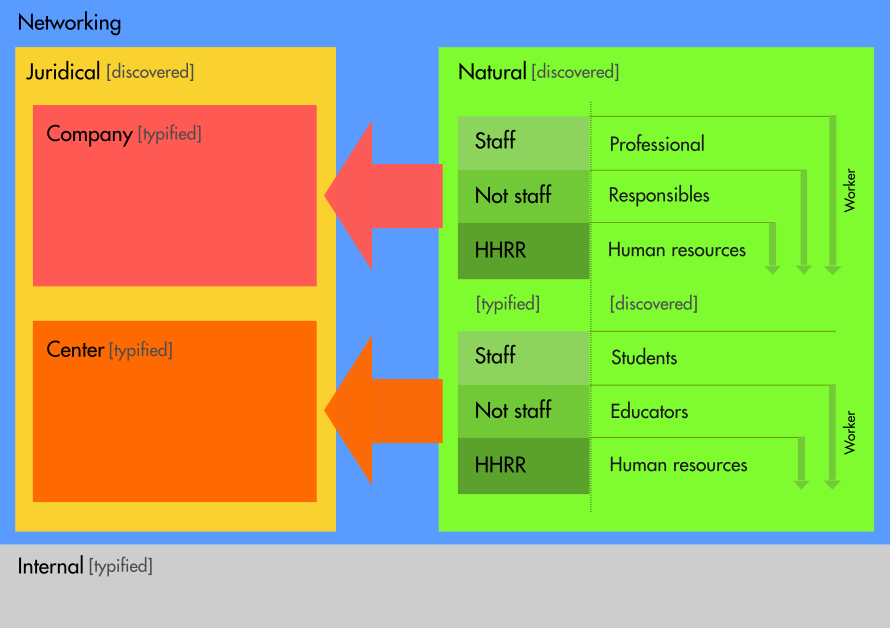
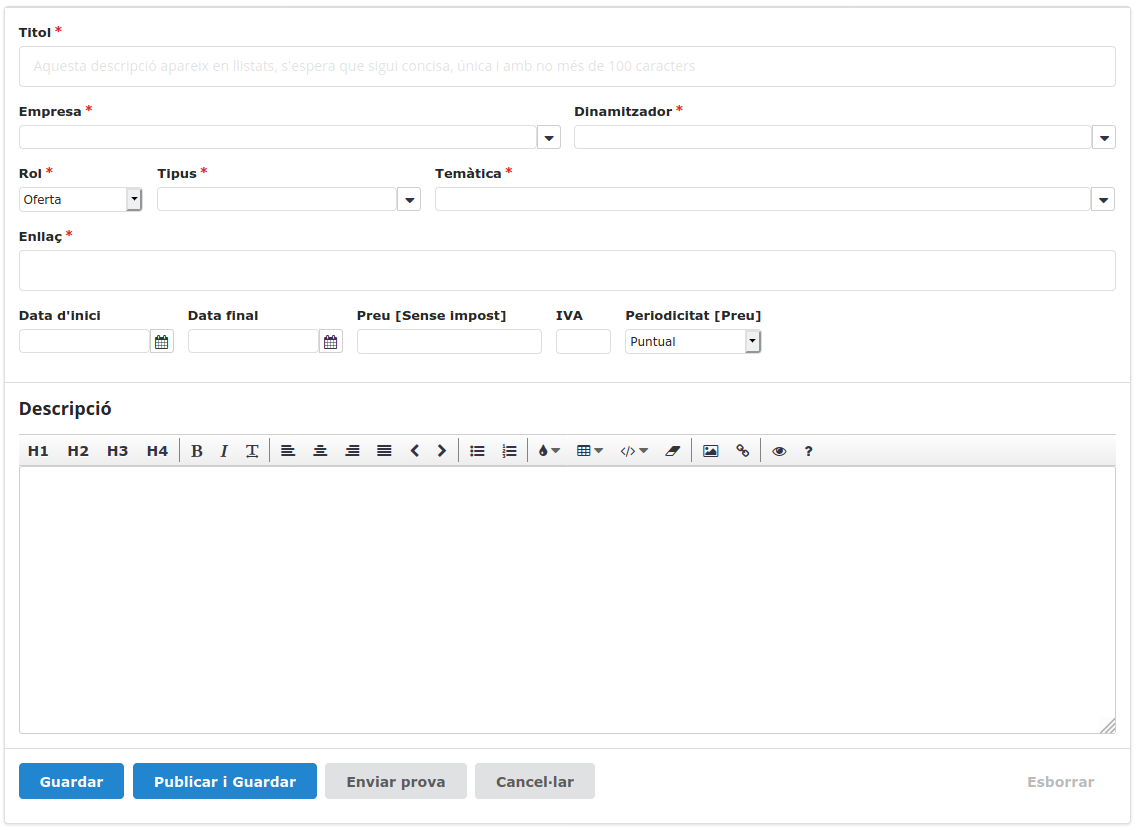





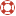





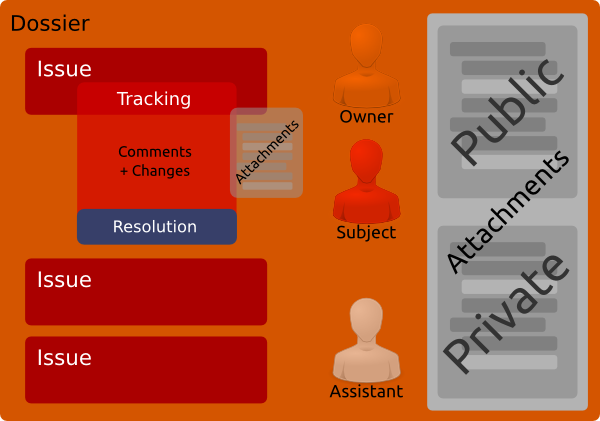
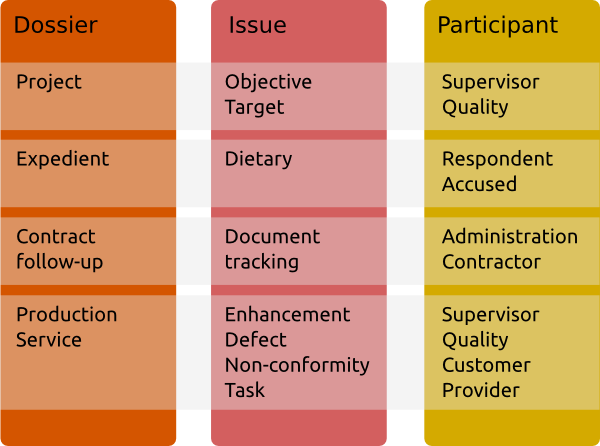
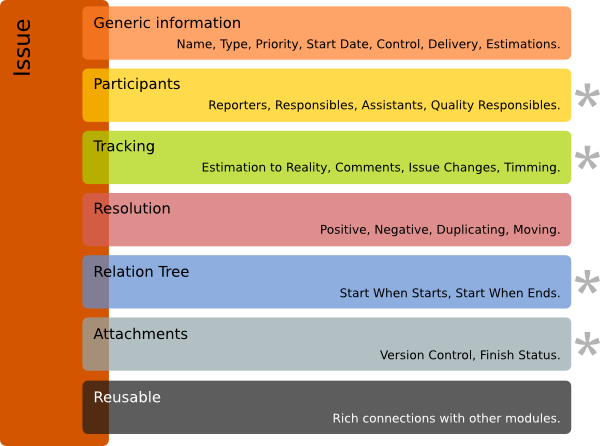
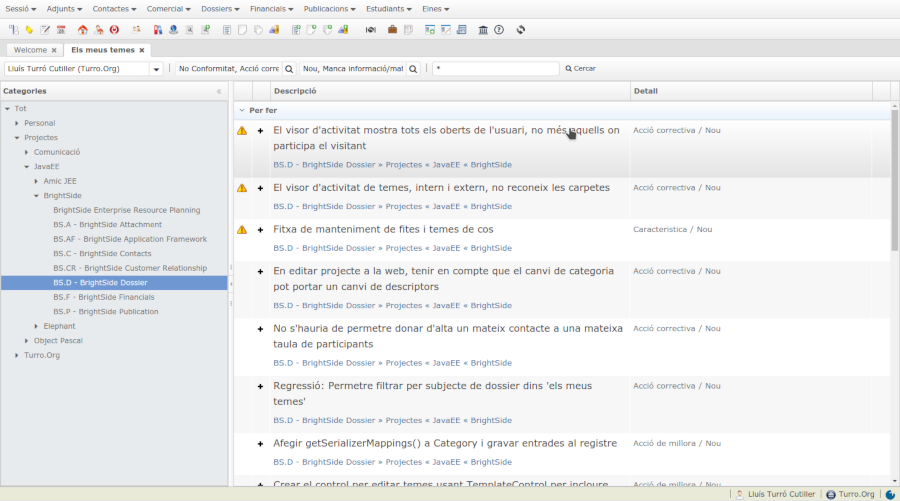
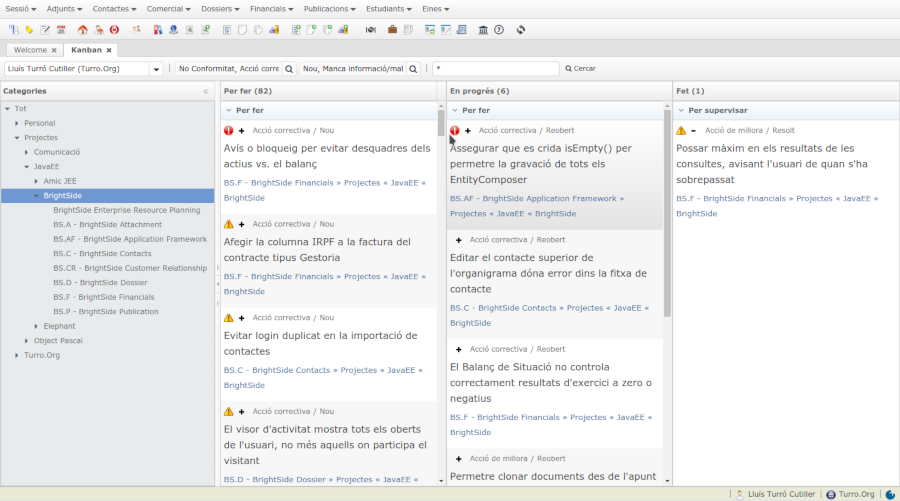
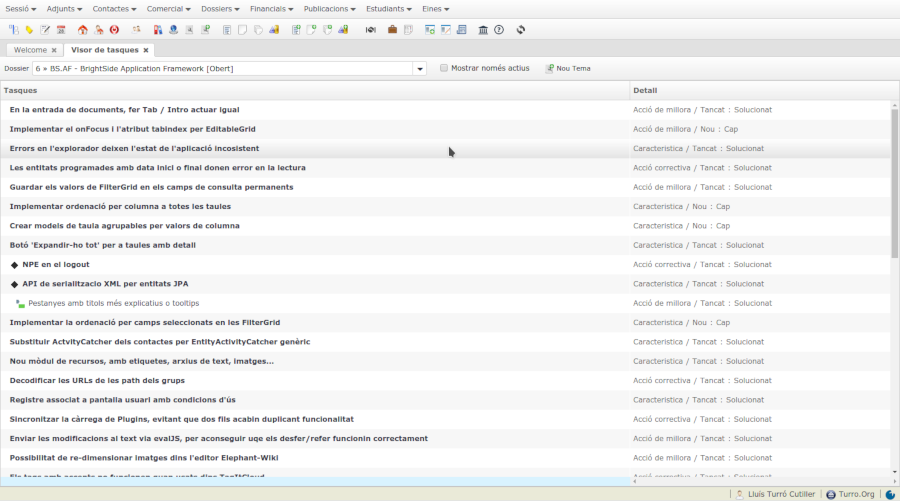

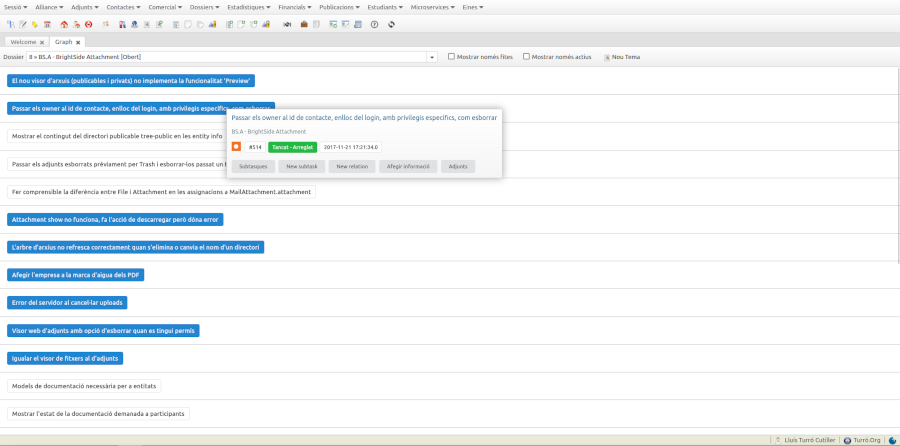
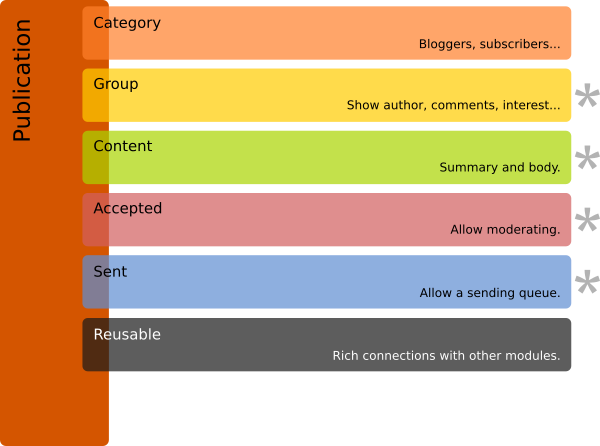
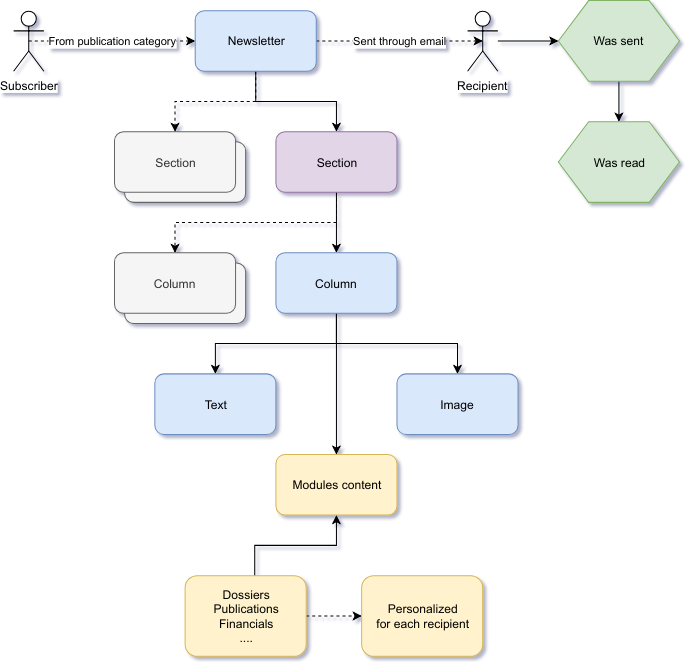
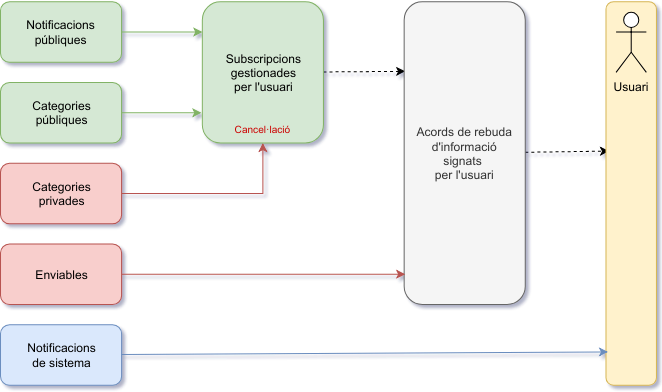
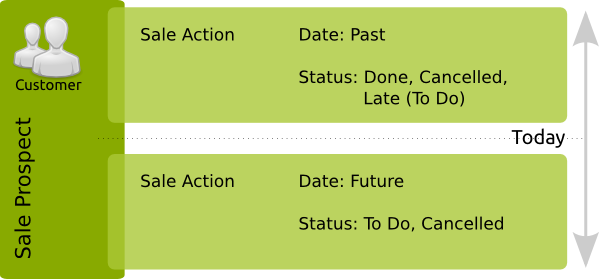

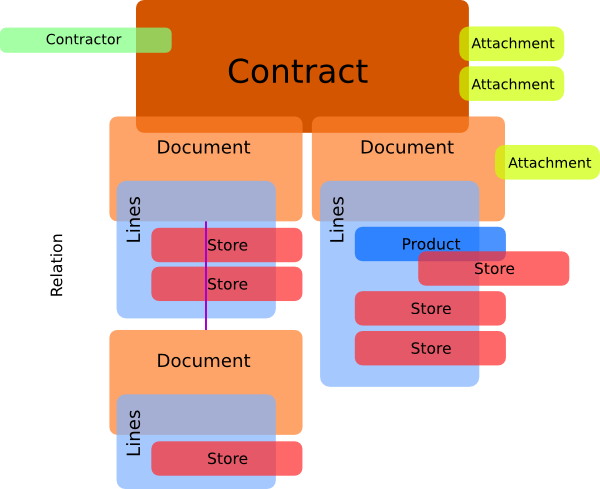
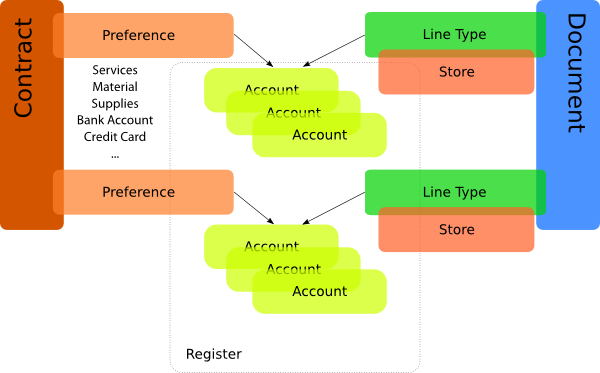
 .
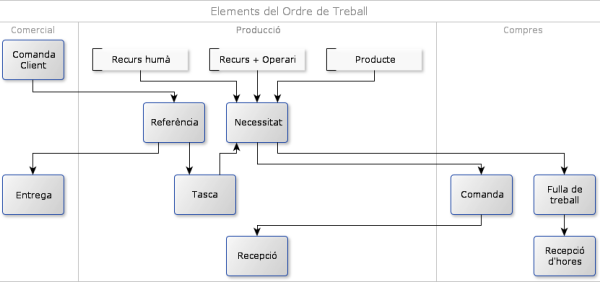
.
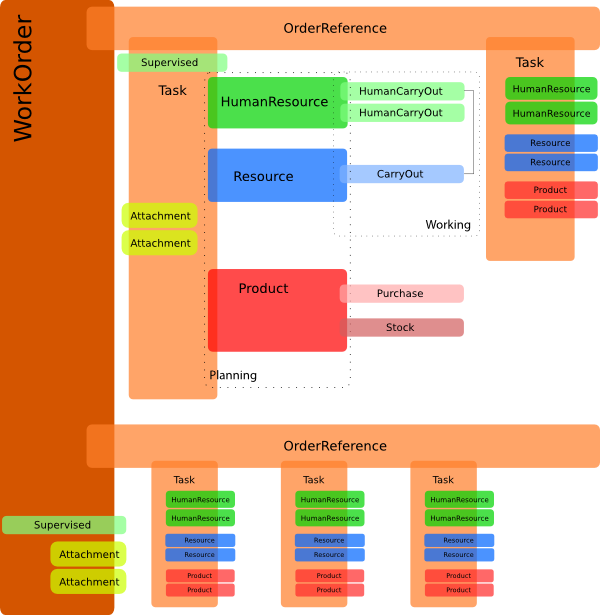
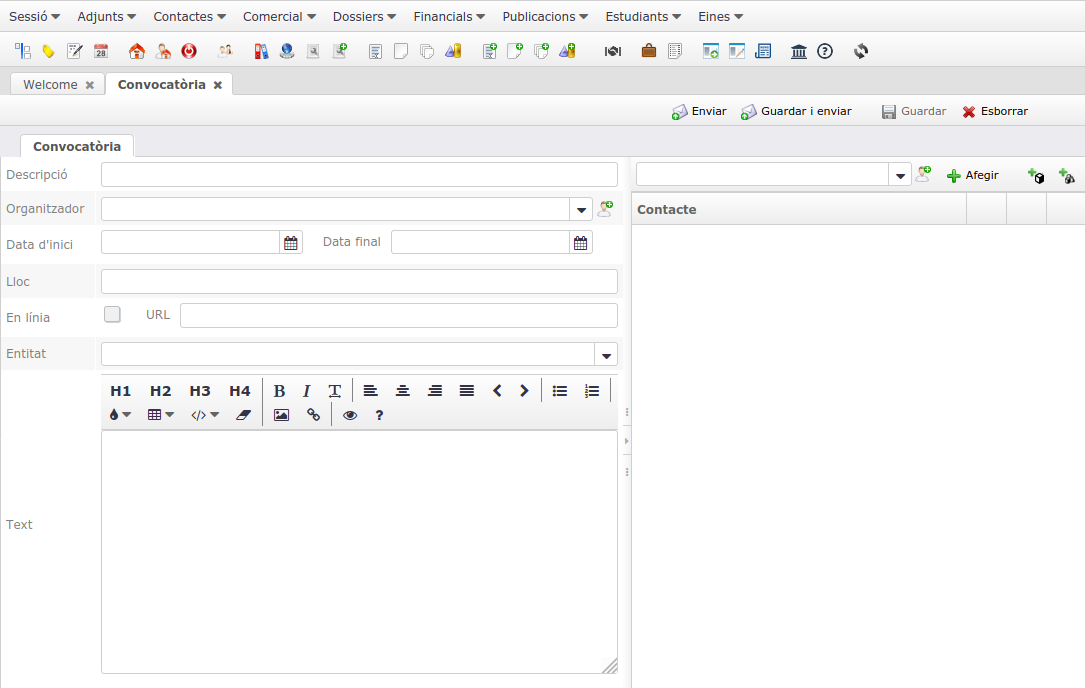

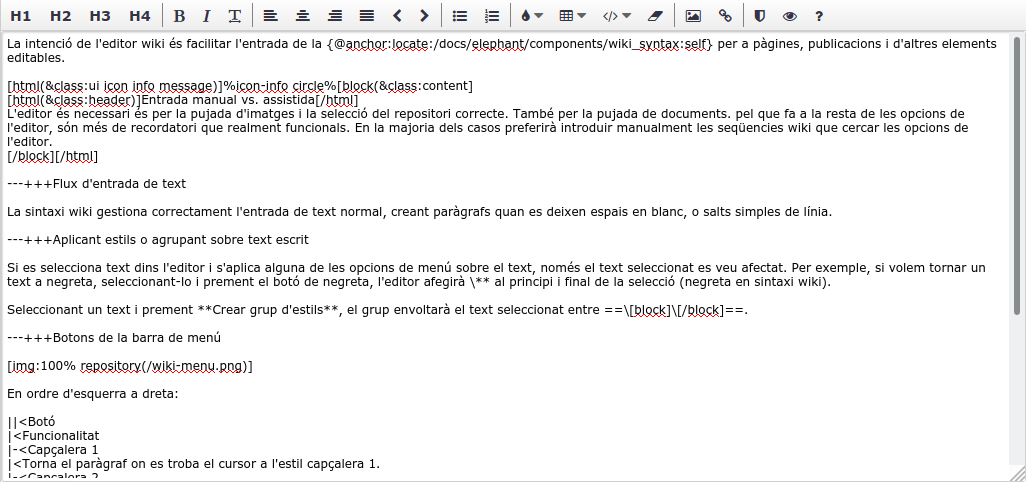

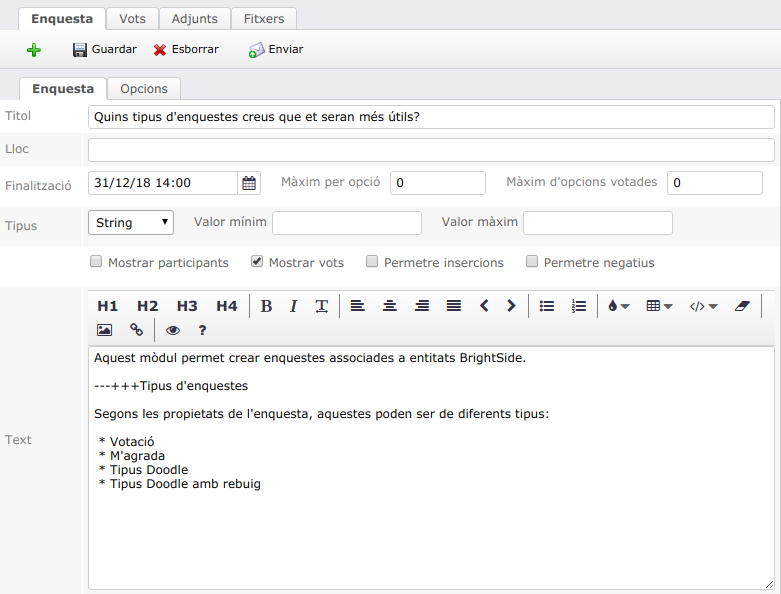

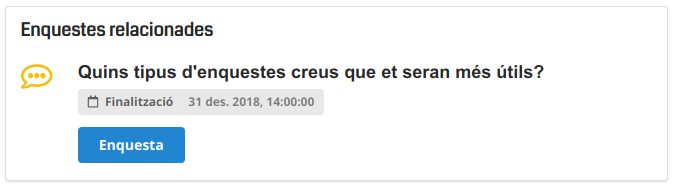
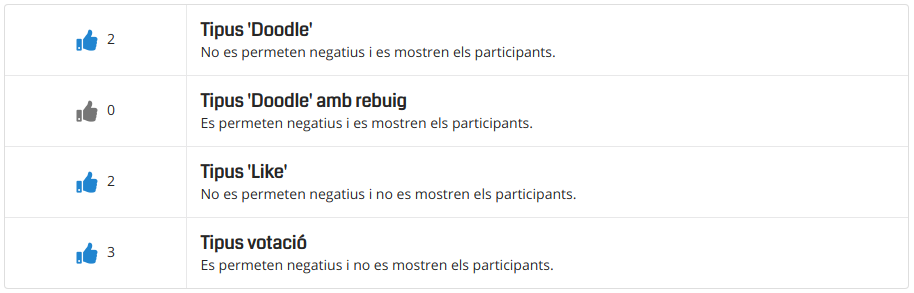
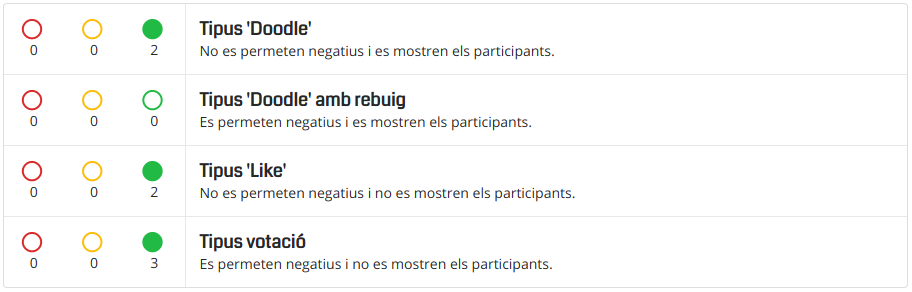
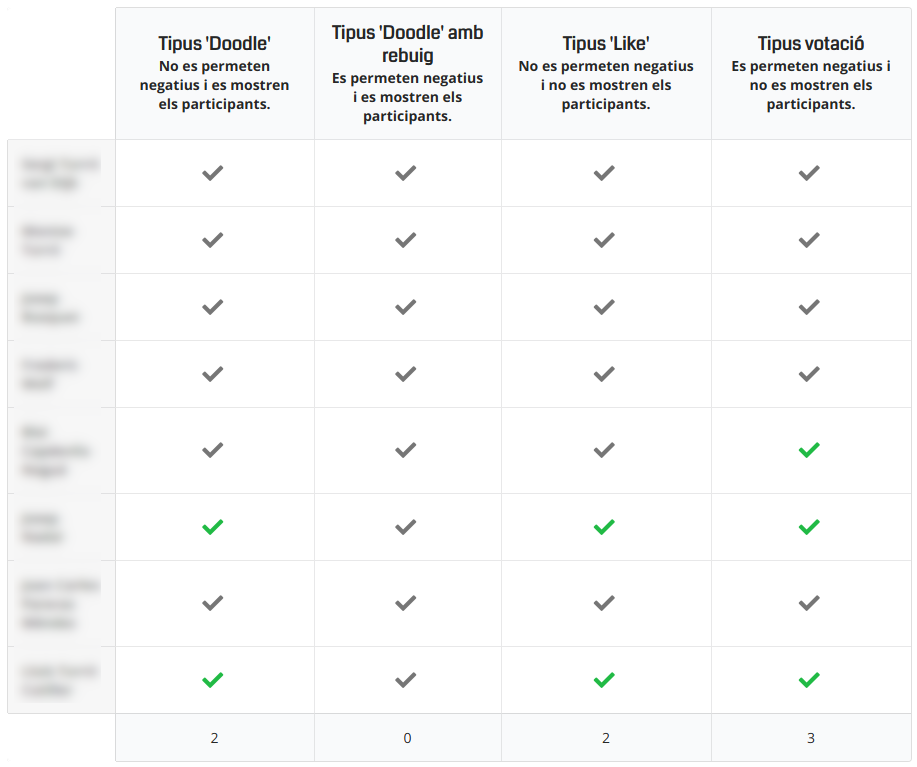
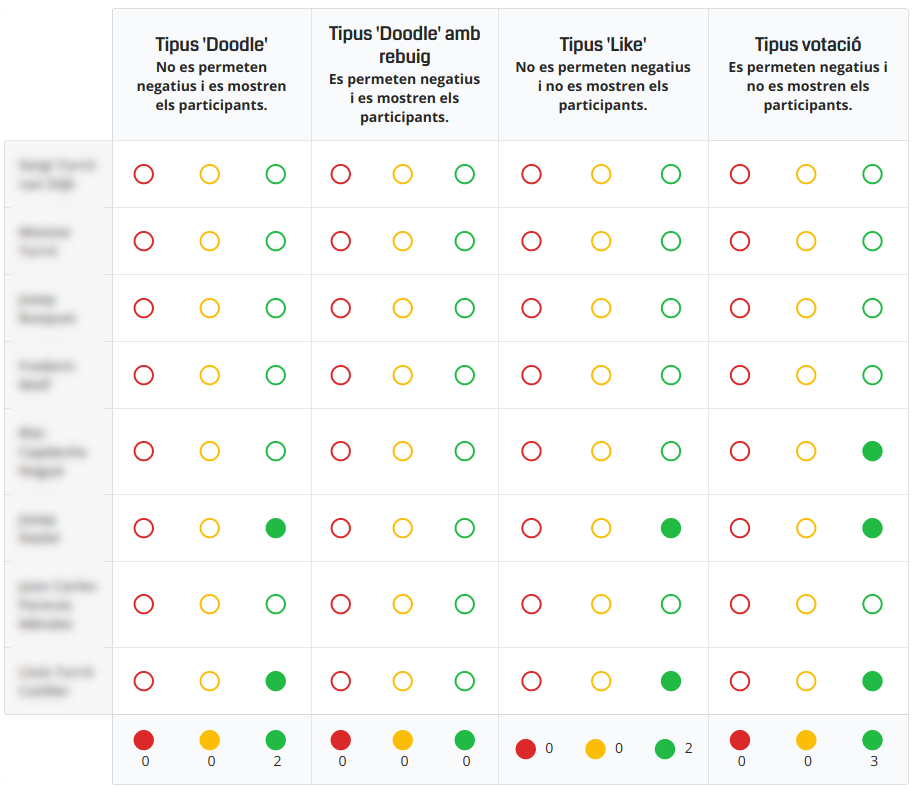
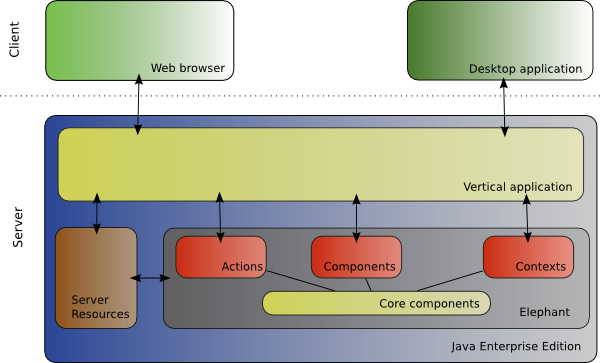
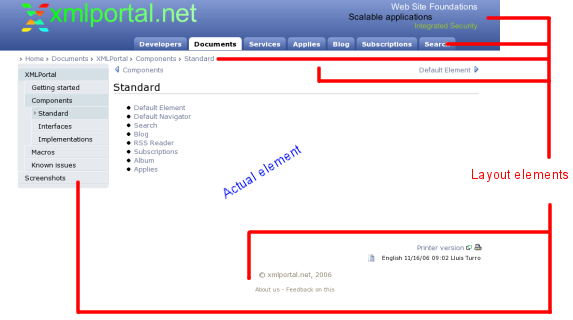
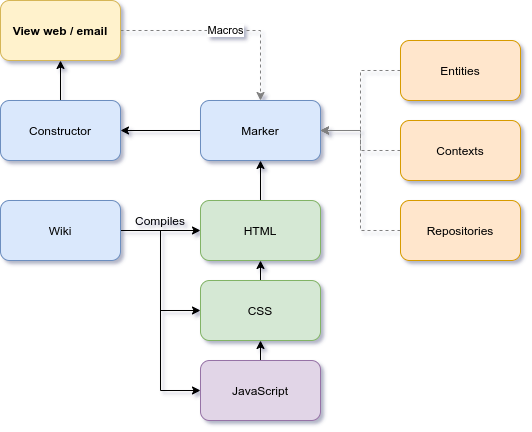



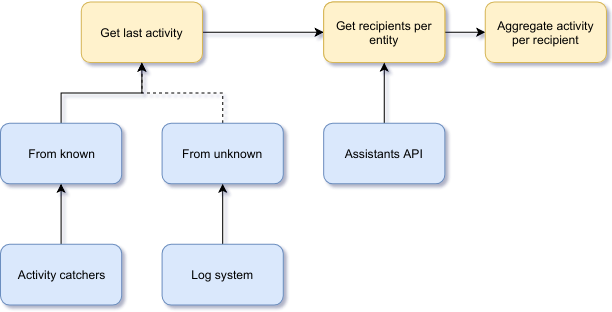
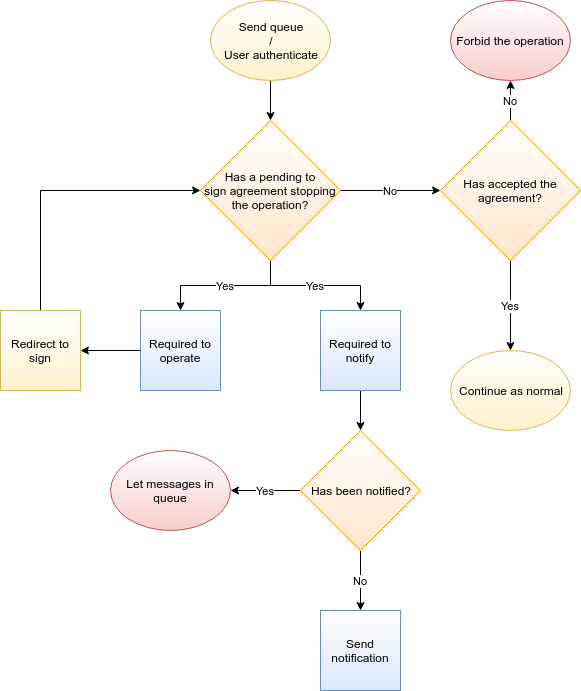


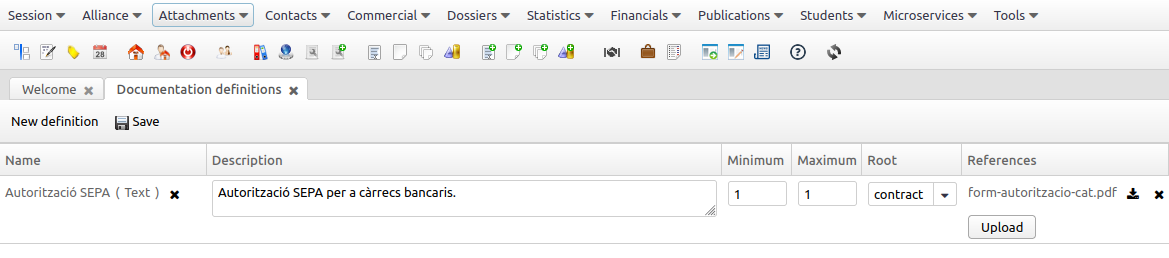
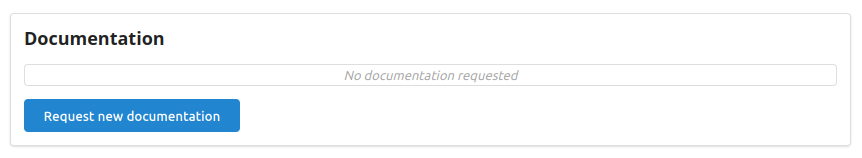
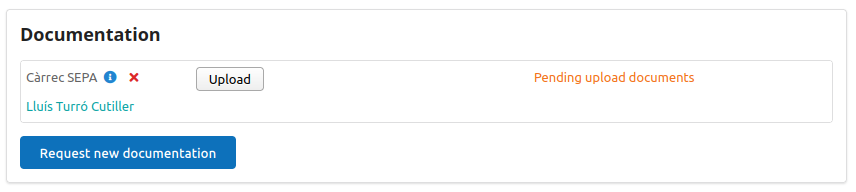
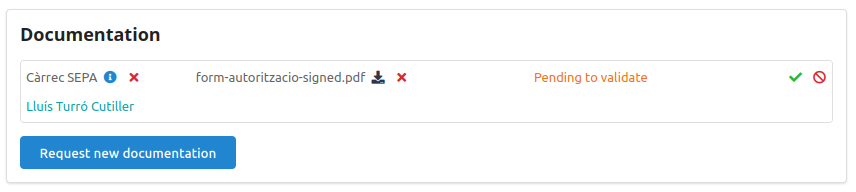
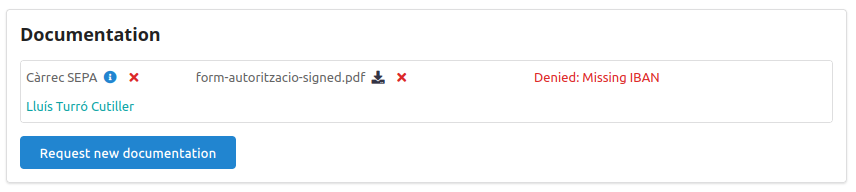
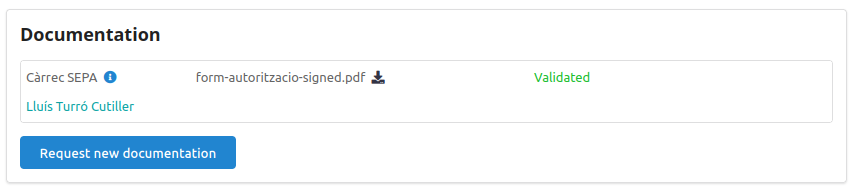
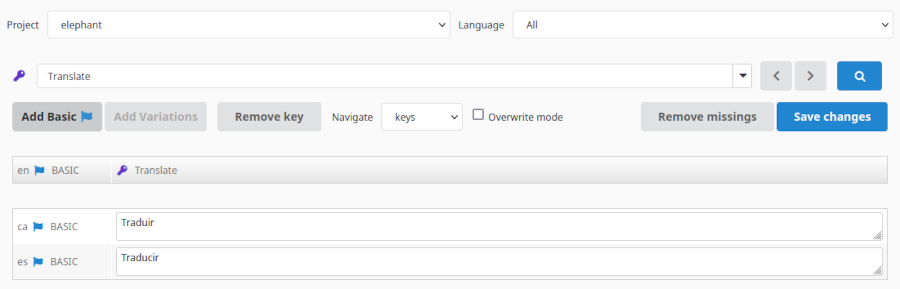
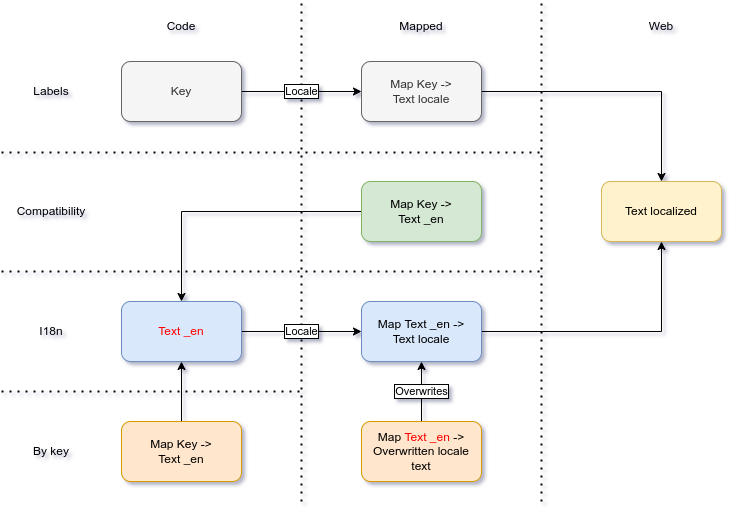
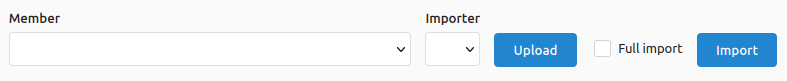
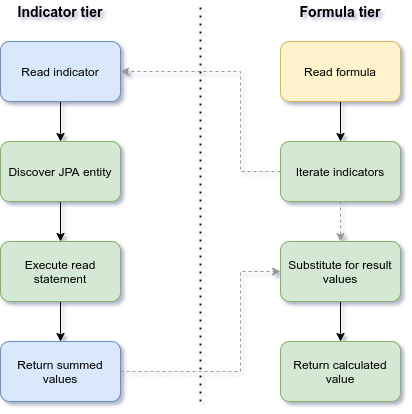
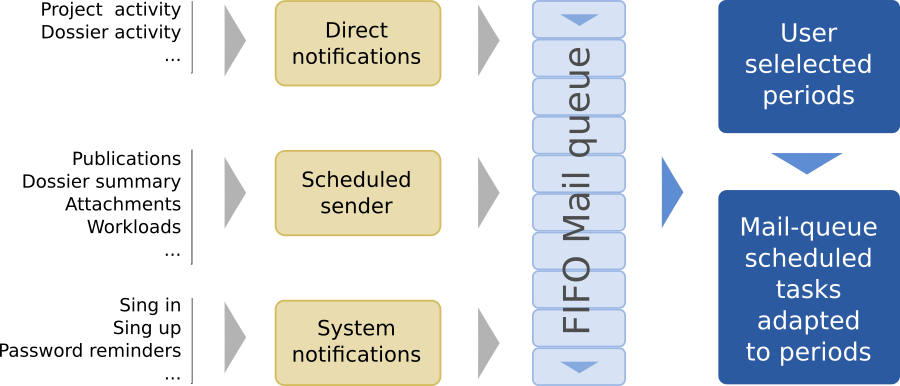
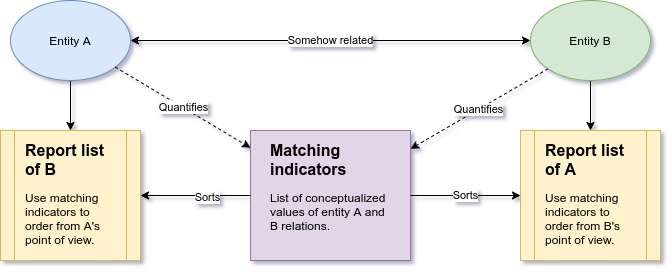
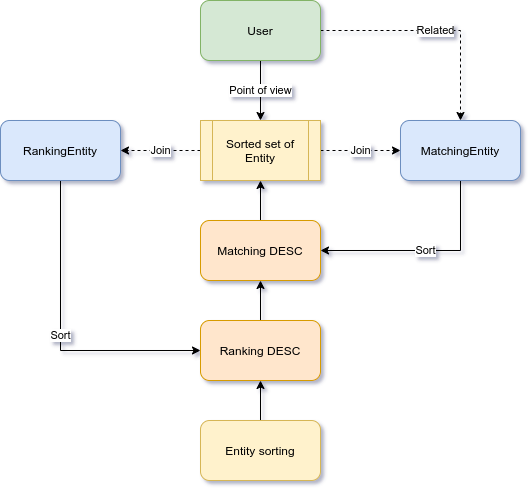



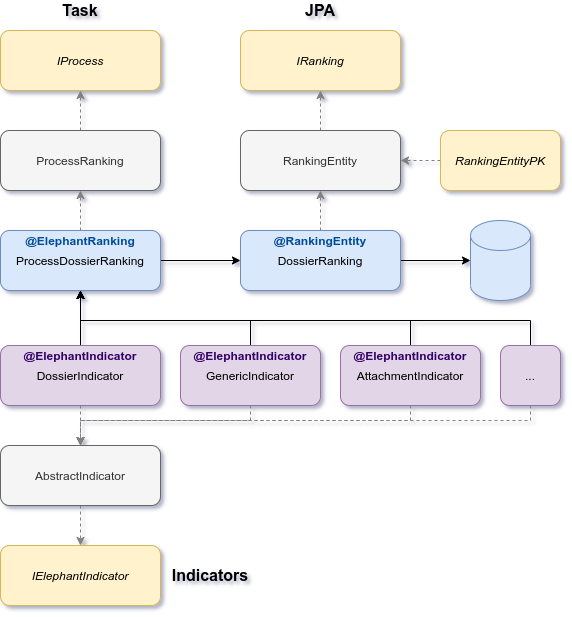


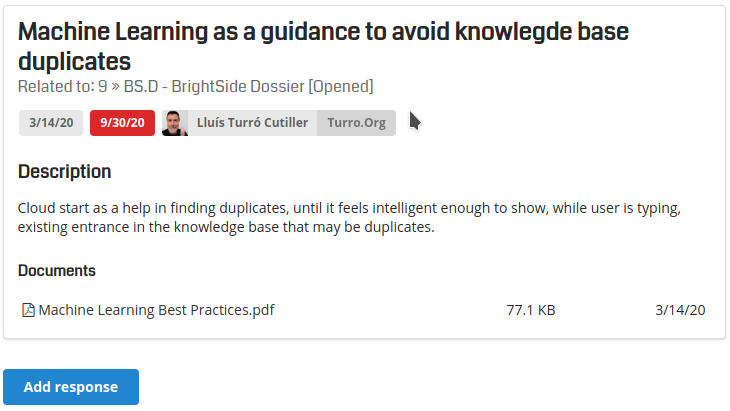

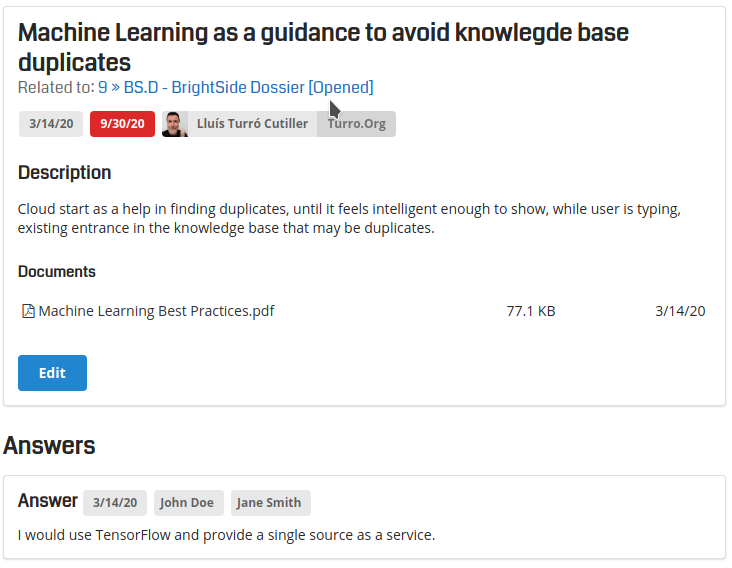


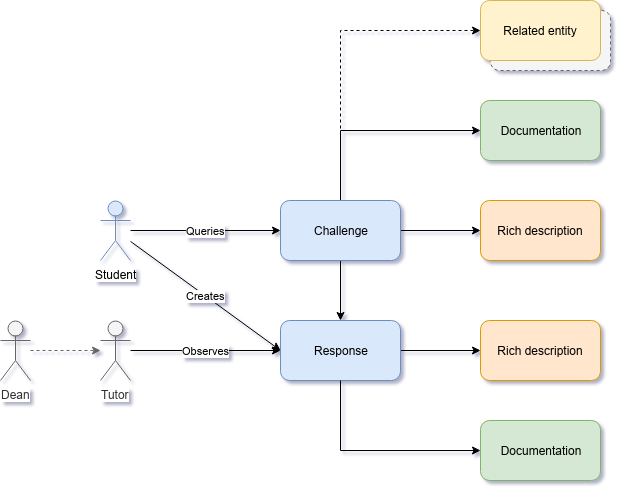



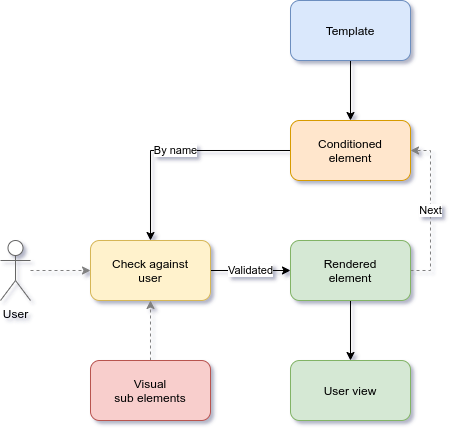






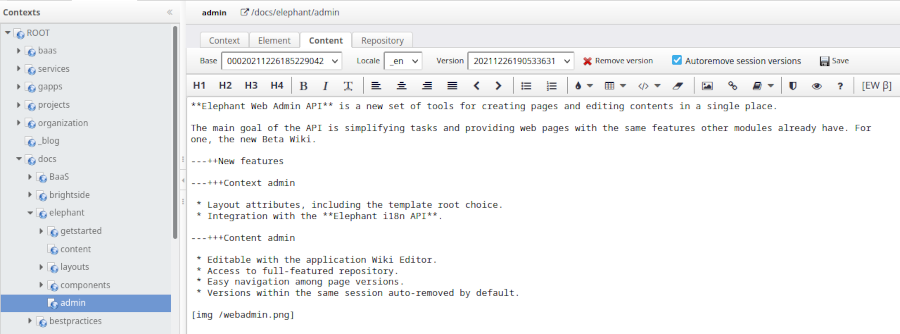
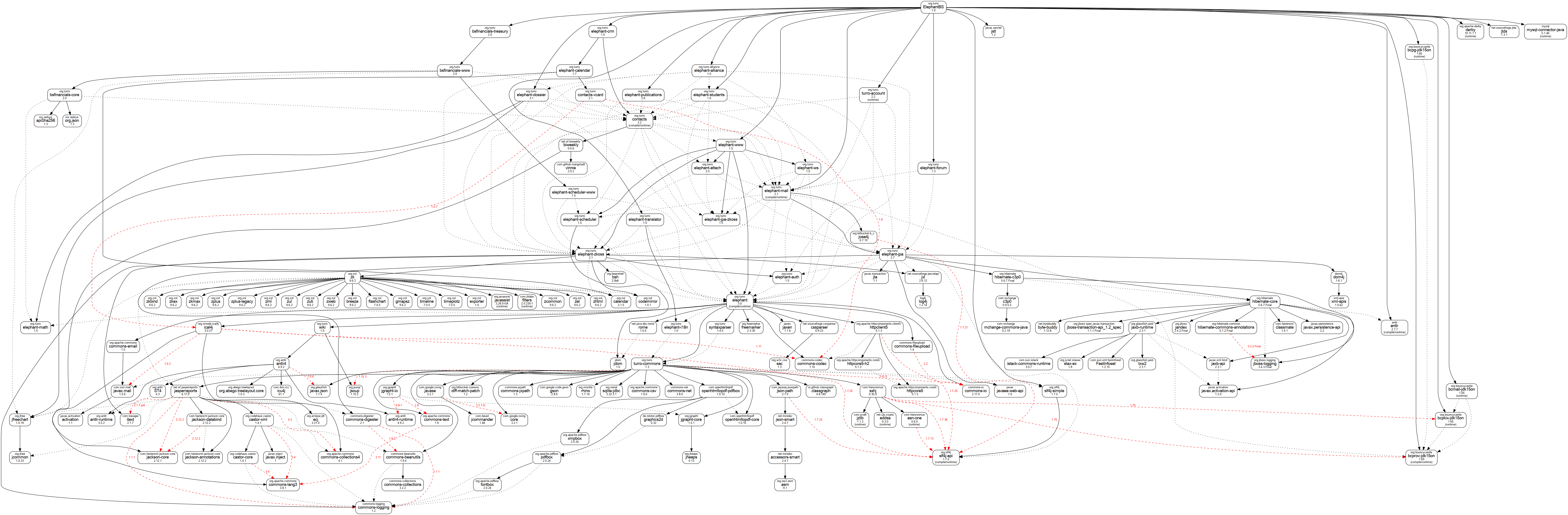
 Video Tutorials
Video Tutorials