The Visual Elements API provides an affordable way to create views with user sensible data. Visual Elements relies on names given to those parts to be controlled.
The most common example arises when creating a template that needs to know who is viewing it, so can render more or less content. With Visual elements you will give a name to the sensible parts and create a configuration file. The API will do the rest.
Visual Elements is stored as a JSON file in /WEB-INF/elephant/conf and can be edited using BaaS -> Tools -> Files -> Configuration -> JSON.
Controlled attributes against user
Every visual element will be checked against user his allowed social groups, grouping values, administration attributes. As a result, the API will tell if the user can have access to the element or is a simple visitor (an authenticated user with no specific permissions for the element).
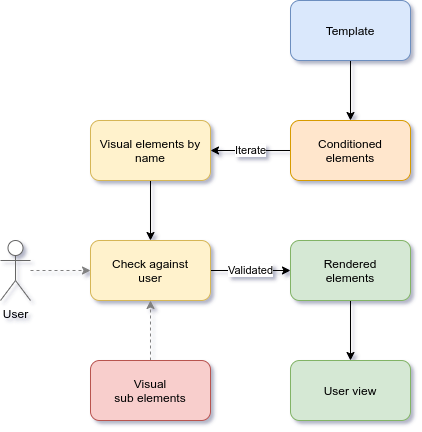
First case, insert by iteration
The method allowed(user) returns a sorted collection of allowed elements for user. Inside the template you will iterate the collection, check its name and insert the content. The sort order is also part of the API and is specified in the configuration file.
The image gives a very simplified example of iteration. Does not show how to implement the iteration within the template. Usually you will check the visual element name against the expected name for content. Example, if visual-element-name equals content-name then add the content.
Second case, check against the API
Instead of iterating a collection, you can check directly against any given name. The method getElement(name, user) returns, if allowed for user, the visual element with the given name.
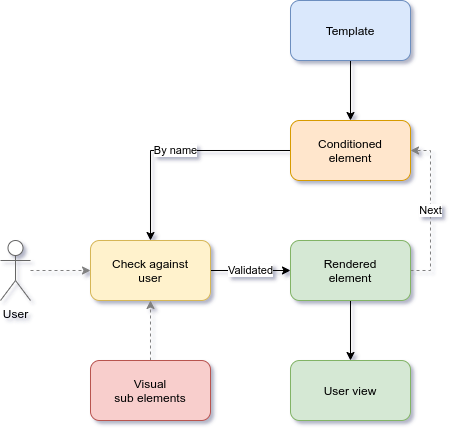
The sub elements
As you probably already noticed, both cases include the possibility of sub elements. A sub element is a visual element that fully depends on its parent. The allows(name, user) returns true when the element name can be shown to user.
To understand sub elements utility, think about form actions. The parent element is an HTML form and the buttons represent actions. Using the API, each button can be conditioned by the allows(action_name, user) method.
Another example, imagine you have a determined list of users. Now, you're not sure whether show user's name and company, or only company's name. And you're quite sure this will be something that will vary among your customers. Using the API, you can relay on an easy to edit configuration file.
Adding specific entities
The whole Elephant system heavily uses entities. Entities are groups of related information and have a full Entities API to relay on. In order to use entities with the Visual Elements API, you need to implement the VisualEntityCheck interface. Consists in a single method check(property, value, entity, user) and returns a boolean.